 |
| 1 |  | 
Gross domestic product can best be described as: |
|  | A) | the total number of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year. |
|  | B) | the market value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year. |
|  | C) | the total number of products produced in the economy. |
|  | D) | the total number of services produced in the economy. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
In a given year, a country's exports total $25 billion and its imports are $27 billion. Its net exports are: |
|  | A) | $52 billion. |
|  | B) | –$2 billion. |
|  | C) | $2 billion. |
|  | D) | $26 billion. |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
The "G" term in C + Ig + G + Xn includes all of the following except: |
|  | A) | state government purchases of new computers. |
|  | B) | Social Security checks received by retirees. |
|  | C) | salaries received by members of the military. |
|  | D) | local government expenditures for new school construction. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
In order from largest to smallest, the components of U.S. expenditures are: |
|  | A) | consumption, net exports, gross investment, and government purchases. |
|  | B) | government purchases, gross investment, consumption, and net exports. |
|  | C) | consumption, government purchases, gross investment, and net exports. |
|  | D) | consumption, government purchases, net exports, and gross investment. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
GDP includes: |
|  | A) | all government spending at all levels. |
|  | B) | all government spending at all levels except the local level. |
|  | C) | government purchases at all levels and federal spending on transfer payments. |
|  | D) | government purchases at all levels, but excluding transfer payments. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
How are intermediate goods treated in the calculation of GDP? |
|  | A) | Only imported intermediate goods are considered. |
|  | B) | Intermediate goods are included in GDP only in the year in which they are produced. |
|  | C) | The value of intermediate goods is not counted separately but is included as part of the value of the final good of which they are an input. |
|  | D) | The value of intermediate goods is counted separately and also included as part of the value of the final good of which they are an input. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Real GDP is found by: |
|  | A) | adding depreciation to nominal GDP. |
|  | B) | adjusting nominal GDP by the GDP price index. |
|  | C) | adding up the dollar value of all transactions in the economy in a given year. |
|  | D) | excluding exports and imports from nominal GDP. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Last year nominal GDP increased by 8 percent while real GDP increased by 10 percent. From this, we can conclude that: |
|  | A) | net investment was positive last year. |
|  | B) | the price level increased last year. |
|  | C) | the price level decreased last year. |
|  | D) | unemployment increased last year. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Refer to the following data: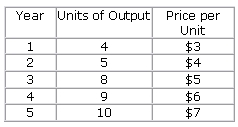 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073511455/991476/ch10_q9.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073511455/991476/ch10_q9.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a>
This economy produces only one product; price and output data are shown for a five-year period. Year 3 is the base year. Real GDP in year 5 is: |
|  | A) | $40 |
|  | B) | $50 |
|  | C) | $56 |
|  | D) | $70 |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Real GDP was $5,000 billion in year 1 and $5,200 billion in year 2. The approximate rate of economic growth from year 1 to year 2 was: |
|  | A) | 0.2 percent. |
|  | B) | 0.4 percent. |
|  | C) | 4 percent. |
|  | D) | $200 billion. |
|
|

