 |
| 1 |  | 
According to the blending model of inheritance a cross between a short plant and a tall plant will always produce __________, while according the particulate model of inheritance this cross will produce __________. |
|  | A) | tall plants; medium height plants |
|  | B) | medium height plants; only short plants |
|  | C) | short plants; medium height plants |
|  | D) | medium height plants; some tall plants and some short plants |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Pea plants were a good plant for Mendel to use in his experiments for all of the following reasons EXCEPT |
|  | A) | the plants are capable of self-pollination. |
|  | B) | the plants are true-breeding. |
|  | C) | the plants have a short generation time. |
|  | D) | the plants produce many offspring. |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Before scientists knew much about genes, Mendel established his law of segregation, which includes astute observations of phenomena that result from the process of meiosis. This law accounted for __________, “factors” inherited from both parents that account for traits. It also accounted for the formation of gametes carrying one “factor” for each trait and then combining during __________ to produce an individual with a combination of factors from the parent generation for each trait. |
|  | A) | homologues; fertilization |
|  | B) | genes; meiosis II |
|  | C) | homologues; meiosis II |
|  | D) | genes; fertilization |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
In genetics, uppercase letters represent dominant traits, which are so named because they __________; lowercase letters represent recessive alleles, or __________. |
|  | A) | are the most frequently occurring form of the trait; those which are least common |
|  | B) | can easily mask the expression of a recessive allele; those which can easily be masked by dominant alleles |
|  | C) | are the most frequently occurring form of the trait; those which can be easily masked by dominant alleles |
|  | D) | can easily mask the expression of a recessive alleles; those which are least common |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
A combination of alleles results from fertilization. For example, the combination of different alleles indicated by the letter A might include AA, Aa, or aa. Which of these genotypes is heterozygous? Homozygous dominant? Homozygous recessive? |
|  | A) | aa, AA, Aa |
|  | B) | AA, Aa, aa |
|  | C) | Aa, AA, aa |
|  | D) | Aa, aa, AA |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
The alleles an individual receives at fertilization are referred to as its __________. The physical appearance of an individual is referred to as its __________. |
|  | A) | genotype; phenotype |
|  | B) | phenotype; genotype |
|  | C) | dominant alleles; recessive alleles |
|  | D) | recessive alleles; dominant alleles |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
The table contains information about the alleles for flower color in a fictitious plant. If a plant that is heterozygous for red flowers is crossed with a plant that is homozygous recessive for yellow flowers, what genotypes and phenotypes can result?
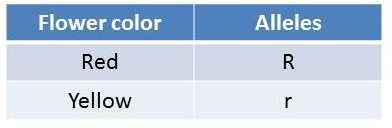 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch10Post_Q7_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (12.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch10Post_Q7_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (12.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | 2 heterozygous(Rr) plants with red flowers and 2 homozygous recessive (rr) plants with yellow flowers |
|  | B) | 3 heterozygous (Rr) plants with red flowers and 1 homozygous recessive (rr) plant with yellow flowers |
|  | C) | 1 homozygous dominant(RR) plant with red flowers, 2 heterozygous(Rr) plants with red flowers, and 1 homozygous recessive (rr) plant with yellow flowers |
|  | D) | 3 homozygous dominant (RR) plants with red flowers and 1 homozygous recessive (rr) plant with yellow flowers |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Mendel developed his law of independent assortment by performing __________ crosses. He discovered that genes separate __________; this information is supported by meiosis, particularly in the random alignment of homologues at the spindle pole. |
|  | A) | single-trait; but are always linked to other genes |
|  | B) | single-trait; without regard to how other separate |
|  | C) | dihybrid; but are always linked to other genes |
|  | D) | dihybrid; without regard to how others separate |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Dihybrid crosses between plants that are heterozygous for two traits produce offspring with a |
|  | A) | 1:2:1 phenotypic ratio. |
|  | B) | 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio. |
|  | C) | 1:1 phenotypic ratio. |
|  | D) | 3:1 phenotypic ratio. |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Gregor Mendel performed testcrosses |
|  | A) | to confirm the phenotype of his F1 generation. |
|  | B) | for no real reason, since the phenotype easily reveals the genotype. |
|  | C) | to confirm the genotype of his F1 generation since he could not be sure just by phenotype. |
|  | D) | to confirm the genotype of his P generation in case he had made a mistake. |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Testcrosses are used to determine genotype because |
|  | A) | all plants can self-pollinate and complicate results. |
|  | B) | it is possible to observe the genotype, but to really figure out the phenotype, you have to run a testcross. |
|  | C) | there is no other way to do it. |
|  | D) | only phenotype can be observed, and if the dominant phenotype is present, the individual can be heterozygous or homozygous dominant in genotype. |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
A Punnett square, used to diagram crosses, can easily be used to demonstrate |
|  | A) | the probability of genotypes, and thus phenotypes. |
|  | B) | the probability of phenotypes, but not genotypes. |
|  | C) | the probability of phenotype only. |
|  | D) | the probability of genotype only. |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
A __________ is used to determine whether a condition is recessive or dominant. If a condition is recessive, only individuals with the __________ genotype have the disorder. |
|  | A) | Punnett square; heterozygous |
|  | B) | Punnett square; homozygous recessive |
|  | C) | pedigree; heterozygous |
|  | D) | pedigree; homozygous recessive |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
Pattern ___________ is the pattern of inheritance for an autosomal dominant disorder. Pattern __________ is the pattern of inheritance for an autosomal recessive disorder. The frequency of each disorder in males and females is __________.
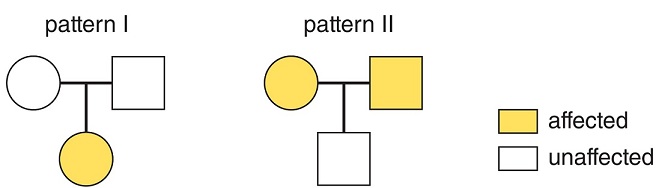 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028595/ch10Post_Q14_resized.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (37.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028595/ch10Post_Q14_resized.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (37.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | I; II; equal because the trait is not sex-linked |
|  | B) | II; I; equal, because the trait is not sex-linked |
|  | C) | I; II; different (higher in males) because the trait is sex-linked |
|  | D) | II; I; different (higher in females) because the trait is sex-linked |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
Which of the following is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder? |
|  | A) | Huntington disease |
|  | B) | neurofibromatosis |
|  | C) | cystic fibrosis |
|  | D) | achondroplasia |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
Which of the following is an autosomal dominant disorder with only one possible genotype? |
|  | A) | cystic fibrosis |
|  | B) | sickle-cell disease |
|  | C) | Huntington disease |
|  | D) | achondroplasia |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
Incomplete dominance is characterized by __________, as in some cases of pigmentation. Codominance is characterized by _________, as in blood type. |
|  | A) | a heterozygote with an intermediate phenotype; two alleles being fully expressed in the presence of one another |
|  | B) | a heterozygote with a dominant phenotype in some offspring and a recessive phenotype in others; three possible alleles for a trait that are all expressed equally |
|  | C) | a heterozygote with an intermediate phenotype; three possible alleles for a trait that are all expressed equally |
|  | D) | a heterozygote with a dominant phenotype in some offspring and a recessive phenotype in others; two alleles being fully expressed in the presence of one another |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
A number of abnormalities are associated with the same allele pair, if the alleles govern production of a protein found in more than one part of the body, for instance, if __________ exists. One trait is associated with more than one allele pair if __________ controls the trait, resulting in a continuous variation of phenotypes. |
|  | A) | incomplete dominance; polyploid alleles |
|  | B) | polyploidy; codominance |
|  | C) | polygenetic inheritance; pleiotropic alleles |
|  | D) | pleiotropy; polygenic inheritance |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
If a recessive trait is transmitted via the X chromosome, or an X-linked recessive allele, its pattern of inheritance is very different than an autosomal recessive trait; this is chiefly because |
|  | A) | males only have one X chromosome, so they cannot express X-linked traits. |
|  | B) | the Y chromosome does not have a corresponding allele, so inheriting a Y chromosome cannot offset an X-linked recessive allele. |
|  | C) | females have two X chromosomes, so X-linked traits are lethal for females. |
|  | D) | males can only receive a Y chromosome from their father. |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
For X-linked recessive disorders, like color-blindness, |
|  | A) | an equal proportion of males and females are affected because the trait is recessive. |
|  | B) | more females than males are affected because they have two X chromosomes. |
|  | C) | more males than females are affected because if they receive a recessive allele from their mother, it is expressed. |
|  | D) | if a woman has the characteristic, her sons do not necessarily have it. |
|
|

