 |
| 1 |  | 
Lamarck offered the idea of inheritance of acquired characteristics. This __________ a satisfactory explanation of evolution, mainly because __________. |
|  | A) | was; it explained why all giraffes have such long necks |
|  | B) | was not; this idea was not supported by experimentation, only observations |
|  | C) | was; this idea was supported by experimentation and observation |
|  | D) | was not; acquired traits are not inherited, only the traits found in the genes can be passed on to offspring |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Which of the following describes natural selection? |
|  | A) | reproduction among bacteria that are able to survive in an environment of antibiotics |
|  | B) | selective breeding of docile silver foxes to produce individuals that allow themselves to be petted and seek attention |
|  | C) | selective reproduction of wild mustard plants with enlarged stems to produce kohlrabi |
|  | D) | choosing an animal or plant to reproduce based on desirable characteristics |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Which of the following is a necessary component of natural selection, as Darwin described it? |
|  | A) | All members of the population survive to reproduce. |
|  | B) | A population can produce only as many offspring as the environment can support. |
|  | C) | Individuals within the population are very similar to one another. |
|  | D) | A population is able to produce more offspring than the environment can support. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
The fossilized dinosaur-like skeleton of Archaeopteryx is a transitional link between early __________ as evident from its long jointed tail, a jaw with teeth, wings, and feathers. |
|  | A) | amphibians and reptiles |
|  | B) | reptiles and birds |
|  | C) | fish and birds |
|  | D) | reptiles and mammals |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Which is the term used to describe anatomical features that are fully developed and functional in one group of organisms but reduced and not functional in similar groups? |
|  | A) | analogous structures |
|  | B) | transitional structures |
|  | C) | vestigial structures |
|  | D) | homologous structures |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Which is the term used to describe anatomical features that are anatomically similar because they are inherited from a common ancestor? |
|  | A) | vestigial structures |
|  | B) | analogous structures |
|  | C) | transitional structures |
|  | D) | homologous structures |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
The wings of birds and insects are |
|  | A) | analogous structures. |
|  | B) | vestigial structures. |
|  | C) | transitional structures. |
|  | D) | homologous structures. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
At some point, all vertebrates |
|  | A) | develop functioning gills. |
|  | B) | have a postanal tail and paired pharyngeal pouches. |
|  | C) | develop ears. |
|  | D) | develop tonsils as well as thymus and parathyroid glands. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
True or False: The presence of analogous structures is evidence that organisms are closely related. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Biogeography, which examines the distribution of plants and animals in different places throughout the world, has revealed |
|  | A) | that unrelated species with the same characteristics may develop in similar environments far away from one another. |
|  | B) | all of these examples to be true. |
|  | C) | that organisms which arose in the same place, but were later separated into isolated populations, may show different diversification patterns because of the other organisms present in the separate locations. |
|  | D) | that populations from the same origin may evolve differently in environments with different food sources. |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Which is an example of molecular homologies, or molecules that are similar because they are inherited from a common ancestor? |
|  | A) | The presence of developmental genes (i.e., Hox genes) in diverse invertebrates and mammals, including humans. |
|  | B) | The presence of the same genes and proteins between and among individuals of different species. |
|  | C) | The presence of DNA (or RNA) and ATP in all cells. |
|  | D) | All of these are examples of molecular homologies. |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
True or False: Relatedness between organisms can be correlated to the number of amino acid differences when comparing proteins that exist in different types of organisms. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
In reality, the Hardy-Weinberg principle |
|  | A) | holds in all cases. |
|  | B) | holds unless there is human interference with naturally breeding populations. |
|  | C) | does not hold because dominance causes an allele to become more common. |
|  | D) | does not hold because the conditions are rarely, if ever, met. |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
Which phenomenon provides new alleles, and therefore underlies all other mechanisms that produce variation? |
|  | A) | random mating |
|  | B) | speciation |
|  | C) | mutation |
|  | D) | microevolution |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
Sexual recombination is just as important as mutation with respect to phenotype because |
|  | A) | it never produces more successful phenotypes. |
|  | B) | it always produces more successful phenotypes. |
|  | C) | it can bring together a new and different combination of alleles. |
|  | D) | it does not bring together new combinations of alleles, which can be detrimental to the survival of existing phenotypes. |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
Assortative mating, a specific type of __________ that occurs between individuals who are phenotypically the same with respect to certain characteristics, changes gene frequency by __________. |
|  | A) | nonrandom mating; driving down the number of individuals that are heterozygous for specific gene loci |
|  | B) | random mating; driving down the number of individuals that are heterozygous for specific gene loci |
|  | C) | random mating; driving up the number of individuals that are homozygous for specific gene loci |
|  | D) | nonrandom mating; driving up the number of individuals that are homozygous for specific gene loci and driving down the number of individuals that are heterozygous for these loci |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
Situation A: A population’s size is drastically reduced via isolation from the general population, increasing the frequency of rare alleles.
Situation B: A population’s size is drastically reduced from habitat loss, creating a group of genetically diverse individuals.
Which phenomenon is described in each situation? Which situation(s) correctly reflect(s) the relationship between population size and the associated influence of genetic drift? |
|  | A) | Situation A describes the founder effect and situation B describes the bottleneck effect; Situation A, because smaller populations like this one are more likely to be affected by genetic drift |
|  | B) | Situation A describes the bottleneck effect and situation B describes the founder effect and situation A, because smaller populations like this one are more likely to be affected by genetic drift |
|  | C) | Situation A describes the founder effect and situation B describes the bottleneck effect; Situation B, because smaller populations like this one are less likely to be affected by genetic drift |
|  | D) | Situation A describes the bottleneck effect and situation B describes the founder effect; Situation B, because smaller populations like this one are less likely to be affected by genetic drift |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
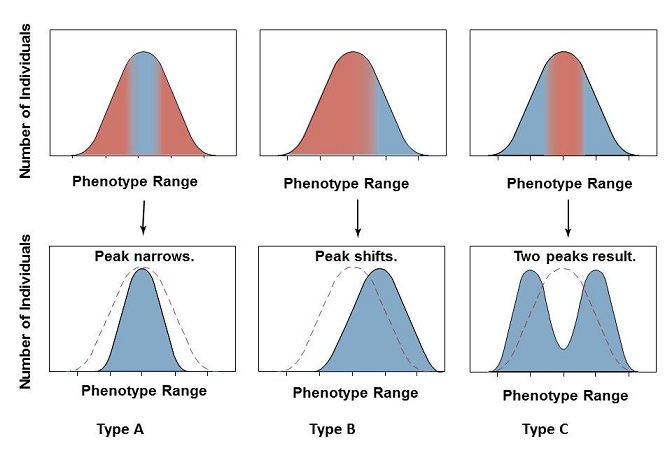
Use the figure to complete this paragraph:
Three types of selection are represented. An extreme phenotype (or more than one) is favored in two types of selection: one extreme phenotype is favored in “Type B” selection, which represents __________ selection; two or more extreme phenotypes are favored over any intermediate phenotype in “Type C” selection, which represents __________ selection. Human birth weight is an example of __________ selection, which occurs when an intermediate phenotype is favored. This is represented in the figure as “Type A”.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028599/ch14Q18_reference.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (64.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028599/ch14Q18_reference.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (64.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | stabilizing; disruptive; directional |
|  | B) | stabilizing; directional; disruptive |
|  | C) | disruptive; stabilizing; directional |
|  | D) | directional; disruptive; stabilizing |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
Sexual selection |
|  | A) | includes adaptive changes in males that lead to an increased chance to mate with a female. |
|  | B) | includes adaptive changes in males and females that lead to an increased chance to reproduce. |
|  | C) | includes adaptive changes in females that lead to an increased chance to mate with a male. |
|  | D) | results in an increased ability to compete with other potential mates. |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
Why is the frequency of the recessive allele for sickle-cell disease declining in the United States, but not in specific regions of the world where malaria is common? |
|  | A) | because there is a heterozygous advantage to carrying the recessive allele in the US, while it protects a person from dying from sickle-cell disease and malaria in regions with frequent malaria infections |
|  | B) | because being homozygous dominant is reproductively advantageous in the densely populated United States, and heterozygotes are slowly declining |
|  | C) | because there is no heterozygous advantage to carrying the recessive allele in the US, while it protects a person from dying from sickle-cell disease and malaria in regions with frequent malaria infections |
|  | D) | because malaria can be quickly treated and cured in the United States |
|
|

