 |
| 1 |  | 
The variety of organic molecules is directly related to the chemistry of carbon. Carbon is the basis of so many different organic molecules because |
|  | A) | carbon can bond with up to six other elements because it has six electrons. |
|  | B) | carbon is small and has four total electrons. |
|  | C) | carbon readily gives up electrons to become a positively charged ion that forms ionic bonds. |
|  | D) | carbon can bond with up to four other elements to complete its outer electron shell. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
There are only four classes of biomolecules in any organism. Which is the correct list of these four classes? |
|  | A) | proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids |
|  | B) | carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and amino acids |
|  | C) | proteins, amino acids, nucleic acids, and nucleotides |
|  | D) | carbohydrates, monosaccharides, lipids, and fatty acids |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Which characteristic below plays the largest role in determining the reactivity of an organic molecule in the body? |
|  | A) | the number of carbon atoms the molecule contains |
|  | B) | the number of hydrogen atoms the molecule contains |
|  | C) | the size of the molecule |
|  | D) | the functional group(s) the molecule contains |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
The figure below depicts two chemical reactions. Which statement below correctly identifies and explains both reactions?
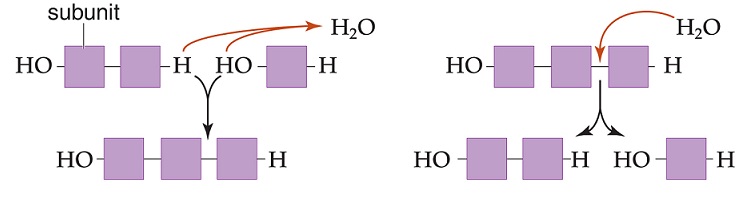 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch03Post_Q4_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (65.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch03Post_Q4_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (65.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | The reaction on the left is a hydrolysis reaction that synthesizes biomolecules. The reaction on the right is a dehydration reaction that degrades biomolecules. |
|  | B) | The reaction on the left is a dehydration reaction that synthesizes biomolecules. The reaction on the right is a hydrolysis reaction that degrades biomolecules. |
|  | C) | The reaction on the left is a dehydration reaction that degrades biomolecules. The reaction on the right is a hydrolysis reaction that synthesizes biomolecules. |
|  | D) | The reaction on the left is a hydrolysis reaction that degrades biomolecules. The reaction on the right is a dehydration reaction that synthesizes biomolecules. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
The “Subunits” column in the table below is scrambled. What is the correct order of the subunits?
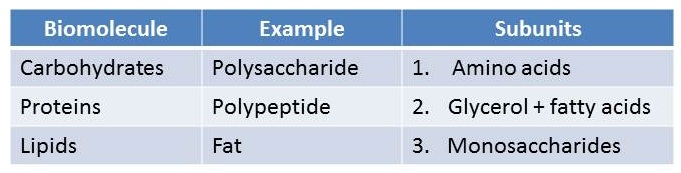 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch03Post_Q5_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (42.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch03Post_Q5_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (42.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | 1,3,2 |
|  | B) | 2,3,1 |
|  | C) | 3,1,2 |
|  | D) | 3,2,1 |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Sweet-tasting sugar molecules with 6-14 carbon molecules that provide quick energy and result from dehydration reactions are called __________. Sweet-tasting, single sugar molecules that have 3-7 carbons and are a quick source of energy are called __________. |
|  | A) | deoxyribose; ribose |
|  | B) | disaccharides; polysaccharides |
|  | C) | ribose; deoxyribose |
|  | D) | disaccharides; monosaccharides |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Complex carbohydrates called polysaccharides have various structures and functions. For instance, some are branched while others aren’t. Some are molecules that provide __________, such as starch and glycogen. Others serve as __________, such as cellulose, chitin, and peptidoglycan. |
|  | A) | short-term energy storage; structural components |
|  | B) | long-term energy storage; structural components |
|  | C) | structural components; short-term energy storage |
|  | D) | structural components; long-term energy storage |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Which of the following choices would correctly label the figure?
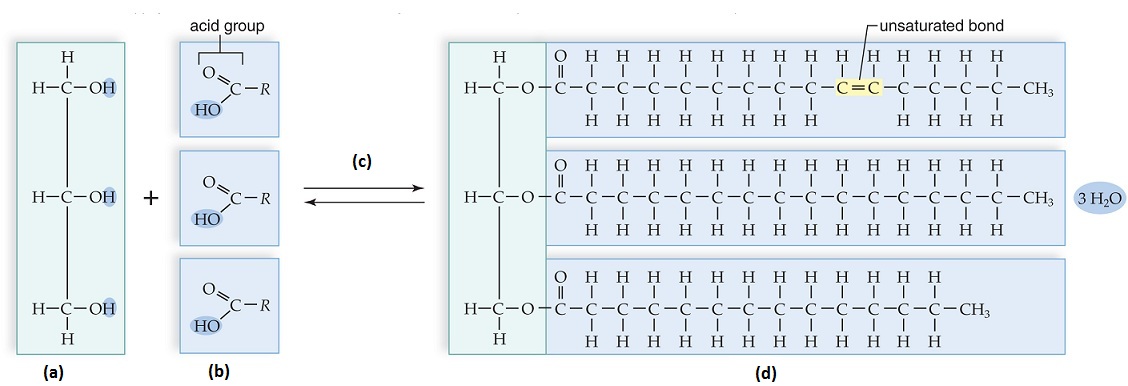 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch03Post_Q8_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (126.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch03Post_Q8_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (126.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | (a) glycerol, (b) three fatty acids, (c) dehydration, (d) three fat molecules |
|  | B) | (a) one triglyceride, (b) three fatty acids, (c) dehydration, (d) one fat molecule |
|  | C) | (a) glycerol, (b) three triglycerides, (c) hydrolysis, (d) three fat molecules |
|  | D) | (a) glycerol, (b) three fatty acids, (c) dehydration, (d) one fat molecule |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Differences in the carbon bonds and number of hydrogen atoms in a fatty acid determine the shape of the chains. __________ are characterized by the presence of double bonds between carbon atoms wherever there are less than two hydrogen atoms per carbon atom. The double bonds in these fatty acids create a bend in the chain that prevents close packing between hydrocarbon chains. __________ are characterized by the presence of only single bonds between carbon atoms and as many hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon as possible. There is no bending in these fatty acid chains, allowing them to pack together tightly. |
|  | A) | Saturated fatty acids; Unsaturated fatty acids |
|  | B) | Unsaturated fatty acids; Saturated fatty acids |
|  | C) | Trans fats; Saturated fatty acids |
|  | D) | Unsaturated fatty acids; Trans fats |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Phospholipids are similar to __________ in structure. However, phospholipids are __________ molecules because glycerol is attached to two fatty acids and one phosphate group. This structure makes for a hydrophilic end and a hydrophobic end, well-suited to the formation of a bilayer in water. |
|  | A) | carbohydrates; polar |
|  | B) | carbohydrates; nonpolar |
|  | C) | fats; polar |
|  | D) | fats; nonpolar |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Steroids have __________ structure when compared to fats. This molecule has a skeleton of __________. |
|  | A) | a very similar; glycerol attached to saturated fatty acids |
|  | B) | an entirely different; long-chain fatty acids attached to long-chain alcohols |
|  | C) | a very similar; glycerol attached to long-chain alcohols |
|  | D) | an entirely different; four fused carbon rings |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
Waxes consist of long-chain fatty acids attached to long-chain alcohols. They are __________ at normal temperatures, and also __________, which makes them waterproof. As such, waxes serve as protective coatings in many plants. |
|  | A) | solid; hydrophobic |
|  | B) | solid; hydrophilic |
|  | C) | liquid; hydrophobic |
|  | D) | liquid; hydrophilic |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
Proteins are a very versatile class of biomolecules. They serve a number of purposes in all kinds of cell types. For instance, antibodies are proteins that serve the purpose of _________, to prevent the destruction of cells. Other proteins, like hormones, function in __________, working as messengers that influence cell metabolism. Proteins such as actin and myosin serve yet another function, ________, allowing muscle cells to contract. |
|  | A) | support; metabolism; transport |
|  | B) | defense; motion; transport |
|  | C) | support; regulation; motion |
|  | D) | defense; regulation; motion |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
Proteins are large biomolecules composed of amino acids. Which choice correctly identifies the general structure of an amino acid as depicted in the figure?
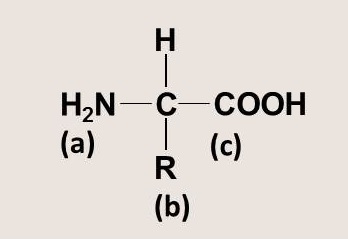 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch03Post_Q14_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (12.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch03Post_Q14_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (12.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | (a) acid group, (b) ribose group, (c) amino group |
|  | B) | (a) amino group, (b) rest of the molecule, (c) acid group |
|  | C) | (a) amino group, (b) ribose group, (c) acid group |
|  | D) | (a) rest of the molecule, (b) acid group, (c) amino group |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
Which of the indicated bonds in a peptide bond, the characteristic covalent bond between two amino acids, and why is it polar?
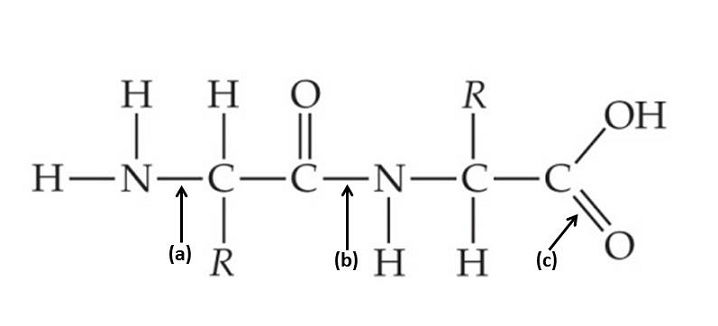 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch03Post_Q15_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (23.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch03Post_Q15_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (23.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | bond “(c)”; The bond is polar because the atoms of the bond share the electrons evenly. The carbon and oxygen attract the electrons equally. |
|  | B) | bond “(b)”; The bond is polar because the atoms of the bond share the electrons evenly. The carbon and nitrogen attract the electrons equally. |
|  | C) | bond “(b)”; The bond is polar because the atoms of the bond share the electrons unevenly. The carbon and nitrogen attract the electrons unequally. This is because the oxygen bonded to the nitrogen is slightly negative, while the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen is slightly positive. |
|  | D) | bond “(a)”; The bond is polar because the atoms of the bond share the electrons unevenly. The carbon and nitrogen attract the electrons unequally. This is because the hydrogen bonded to the nitrogen is slightly negative, while the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen is slightly positive. |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
Protein structure determines its function. There are four distinct levels of protein organization. Which choice matches all four levels to the characteristics of that level? |
|  | A) | primary: linear sequence of amino acids that form the polypeptide; secondary: three-dimensional shape due to covalent, ionic, and hydrogen bonding of R groups; tertiary: orientation in space due to hydrogen bonding; quaternary: arrangement of more than one polypeptide in a single protein |
|  | B) | primary: linear sequence of amino acids that form the polypeptide; secondary: orientation in space due to hydrogen bonding; tertiary: arrangement of more than one polypeptide in a single protein; quaternary: three-dimensional shape due to covalent, ionic, and hydrogen bonding of R groups |
|  | C) | primary: arrangement of more than one polypeptide in a single protein; secondary: orientation in space due to hydrogen bonding; tertiary: three-dimensional shape due to covalent, ionic, and hydrogen bonding of R groups; quaternary: linear sequence of amino acids that form the polypeptide |
|  | D) | primary: linear sequence of amino acids that form the polypeptide; secondary: orientation in space due to hydrogen bonding; tertiary: three-dimensional shape due to covalent, ionic, and hydrogen bonding of R groups; quaternary: arrangement of more than one polypeptide in a single protein |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
DNA is a __________-stranded polymer of nucleotides that contains the bases __________ and the sugar__________.
RNA is a __________-stranded polymer of nucleotides that contains the bases __________ and the sugar __________. |
|  | A) | (double; A,G,T,C; deoxyribose) (single; A,G,U,C; ribose) |
|  | B) | (single; A,G,U,C; ribose) (double; A,G,T,C; deoxyribose) |
|  | C) | (double; A,G,U,C; deoxyribose) (single; A,G,T,C; ribose) |
|  | D) | (single, A,G,U,C; deoxyribose) (double; A,G,T,C; ribose) |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
Coded genetic information is __________ in DNA molecules. These molecules combine to form genes, the hereditary units that are passed from parents to their offspring. RNA is synthesized from DNA, one gene at a time. RNA is present in three forms. One form, called messenger RNA (mRNA) determines __________. |
|  | A) | copied; the sequence of nucleotides in nucleic acids |
|  | B) | stored; the sequence of nucleotides in nucleic acids |
|  | C) | copied; the sequence of amino acids in a protein |
|  | D) | stored; the sequence of amino acids in a protein |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
True or False: A genetic mutation is a mistake in the sequence of bases in a gene and can result in an altered amino acid sequence in a protein. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
The energy-carrying ability of ATP molecules can be attributed to |
|  | A) | the covalent bond between ribose and adenine. |
|  | B) | the hydrogen bond between the last two phosphates. |
|  | C) | the instability of the bonds linking the phosphates with each other. |
|  | D) | the covalent bond between ribose and the first phosphate. |
|
|

