 |
| 1 |  | 
Which of the following statements is true, based on the tenets of the cell theory? |
|  | A) | Nothing smaller than a cell is alive. |
|  | B) | All organisms are multicellular. |
|  | C) | New organisms are only formed after sperm and egg cells from previously existing organisms combine. |
|  | D) | Unicellular organisms do not exhibit all of the characteristics of life. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Which statement summarizes the explanation of cell size? |
|  | A) | A cell needs a large enough surface area to transport nutrients in and waste out for the volume of the cell. The surface-area-to-volume ratio of a small cell is greater than the surface-area-to-volume ratio of a large cell. |
|  | B) | A cell needs a small surface area to transport nutrients in and waste out for the volume of the cell. The surface-area-to-volume ratio of a small cell is less than the surface-area-to-volume ratio of a large cell. |
|  | C) | A cell needs a large enough surface area to transport nutrients in and waste out for the volume of the cell. The surface-area-to-volume ratio of a small cell is less than the surface-area-to-volume ratio of a large cell. |
|  | D) | A cell needs a surface area equal to its volume to transport nutrients in and waste out. The surface-area-to-volume ratio of a small cell is 1:1, unlike the surface-area-to-volume ratio of a large cell. |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Why are the prokaryotes divided into two groups, domain Bacteria and domain Archaea? |
|  | A) | Bacterial cells are structurally complex, while domain Archaea includes organisms with structurally simple cells. |
|  | B) | These groups are very different in cell size. Domain Bacteria includes organisms with extremely small cells, while domain Archaea includes organisms made up of large cells. |
|  | C) | Bacterial cells have membrane-bounded nuclei, while Archaea do not. |
|  | D) | Though these groups share their lack of a membrane-bounded nucleus, among other characteristics, they have been proven to be very biochemically different through evidence such as comparison of their DNA. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
A bacterium, as shown in this figure, is a prokaryotic cell that is structurally simple. Which of the following correctly identifies the structures labeled below and their functions?
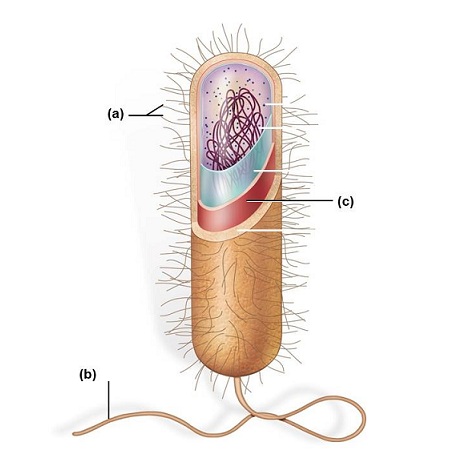 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch04Post_Q4_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (40.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch04Post_Q4_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (40.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | (a) flagellum: allows movement in a fluid medium; (b) pili: allow attachment to solid surfaces; (c) capsule: protects the cell from host defenses |
|  | B) | (a) pili: allow attachment to solid surfaces; (b) flagellum: allows movement in a fluid medium; (c) cell wall: helps to maintain the shape of the cell |
|  | C) | (a) flagellum: allows attachment to a solid surface; (b) pili: allow movement in a fluid medium; (c) plasma membrane: regulates substances moving in and out of the cell |
|  | D) | (a) pili: allow attachment to solid surfaces; (b) flagellum: allows movement in a fluid medium; (c) capsule: protects the cell from host defenses |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Which statement regarding organelles explains their benefit to eukaryotic cells? |
|  | A) | Eukaryotic cells are the same size as prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are able to operate more efficiently than prokaryotic cells because they are more complex because of their organelles. |
|  | B) | Eukaryotic cells are larger than prokaryotic cells. This means they have less surface area per volume. The organelles, which are embedded in the membrane, increase the surface area of the membrane. |
|  | C) | Eukaryotic cells are larger than prokaryotic cells. This means they have less surface area per volume. Organelles function to divide the larger volume up into compartments, making metabolism more efficient. |
|  | D) | Eukaryotic cells are the smaller than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are divided into compartments called organelles in order to decrease their surface-area-to-volume ration. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Animal cells may contain which organelle(s)? |
|  | A) | chloroplast(s) |
|  | B) | a large central vacuole |
|  | C) | a cell wall |
|  | D) | lysosome(s) |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
The eukaryotic nucleus contains the cell’s DNA, which is present as a network of __________ when a cell is not dividing. The DNA and proteins condense to form distinguishable __________ during cell division. |
|  | A) | chromatin; chromosomes |
|  | B) | chromosomes; chromatin |
|  | C) | ribosomes; chromatin |
|  | D) | chromosomes; ribosomes |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Which paragraph below best explains how the nucleus controls the function of the ribosomes? |
|  | A) | The nucleus is the control center of the cell because it is located in the middle and sends out messages, like a brain, to make the other organelles do their jobs. |
|  | B) | The ribosomes are found inside the nucleus. They are only released when the nucleus signals foretells them to go into the cytoplasm and make proteins. |
|  | C) | When assembly of a protein is required, a cell’s DNA condenses into chromosomes and leaves the nucleus via the nuclear pores. It travels to the ribosomes where it remains for the duration of protein production, and then returns to the nucleus where it reverts to its less condensed form, chromatin. |
|  | D) | The genes contain the cell’s instructions for making proteins and the genes are composed of DNA molecules. Since the ribosomes make the proteins, and the instructions come from the DNA in the genes found in the nucleus, the nucleus is essentially in charge of signaling production by the ribosomes. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
The production of an organelle or plasma membrane, many proteins, as well as lipids, takes place in the __________. Final modifications are made to these structures and molecules in the __________, which then sends them off to their final destination in the cell. |
|  | A) | rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (RER); nucleus |
|  | B) | rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (RER and SER); Golgi apparatus |
|  | C) | smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER); Golgi apparatus |
|  | D) | ribosomes; nucleus |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
What is the function of lysosomes? |
|  | A) | production of proteins under the direction of RNA |
|  | B) | isolation and transport of biomolecules |
|  | C) | recycling cellular materials and digesting old organelles |
|  | D) | storage of biomolecules and wastes |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
The endomembrane system includes the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and transport vesicles. What is the function of transport vesicles? |
|  | A) | They break down debris, large biomolecules, and old organelles. |
|  | B) | They are filled with ribosomes, thus they are the sight of protein production. |
|  | C) | They sort and package proteins before those proteins are sent off to their cellular destinations. |
|  | D) | They carry proteins from the ER to the Golgi apparatus, and from the Golgi apparatus to many other destinations. |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
The endomembrane system includes the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and transport vesicles. What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)? |
|  | A) | The rough ER is studded with ribosomes and thus produces proteins; it also forms transport vesicles. The smooth ER produces lipids and forms transport vesicles. |
|  | B) | It sorts and packages proteins before they are sent off to their cellular destinations. |
|  | C) | The rough ER produces proteins under the direction of the RNA. The smooth ER breaks down fatty acids. |
|  | D) | The rough ER regulates the passage of molecules in and out of the cell. The smooth ER helps maintain the shape of the cell. |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
Vacuoles are membranous sacs that are similar to vesicles, but __________. A comparison of the vacuoles in protist and plant cells would demonstrate that _____. |
|  | A) | smaller; these structures perform the same function for both cell types |
|  | B) | larger; these structures perform the same function for both cell types |
|  | C) | smaller; these structures serve different functions in each of these cell types |
|  | D) | larger; these structures serve different functions in each of these cell types |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
Peroxisomes are membrane-enclosed vesicles that contain enzymes. They have varied functions, but basically serve to ____________________; the actions of their enzymes result in the production of __________. |
|  | A) | break down large biomolecules and old organelles; ATP |
|  | B) | break down toxic substances and synthesize needed substances; hydrogen peroxide |
|  | C) | produce carbohydrates using solar energy; carbohydrates |
|  | D) | produce ATP using water and oxygen; hydrogen peroxide |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are _________ reactions. |
|  | A) | identical |
|  | B) | unrelated |
|  | C) | opposite |
|  | D) | oxygen-dependent |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
The chloroplasts are the source of __________. Mitochondria are the source of __________. |
|  | A) | ATP molecules; glucose |
|  | B) | solar energy; glucose |
|  | C) | usable energy for cells; all food for organisms |
|  | D) | all food for organisms; usable energy for cells |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
What are the three different types of fibers that comprise the cytoskeleton? |
|  | A) | motor molecules, actin filaments, and microtubules |
|  | B) | actin filaments, myosin, and microtubules |
|  | C) | actin filaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments |
|  | D) | motor molecules, microtubules, and centrioles |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
The cytoskeleton is a dynamic structure of protein fibers that determines a cell’s shape and keeps its organelles in place while allowing them to move. Flagella and cilia are external whip-like projections of cells that function in cellular movement. What do these have in common? |
|  | A) | microtubules |
|  | B) | centrioles |
|  | C) | intermediate filaments |
|  | D) | actin filaments |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
Centrioles may be related to flagella. How so? |
|  | A) | Centrioles support cells and determine their shape. |
|  | B) | Centrioles distribute chromosomes in an orderly manner. |
|  | C) | Centrioles probably help organize the spindle. |
|  | D) | It is possible that centrioles give rise to a structure that organizes the microtubules in flagella. |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
Myosins, dyneins, and kinesins are __________ that break down ATP and use the resulting energy to change shape and move from one binding site to another. They are associated with movements like muscle contraction, white blood cell “crawling”, and the microtubules that comprise the locomotive cilia and flagella. |
|  | A) | intermediate filaments |
|  | B) | motor molecules |
|  | C) | actin filaments |
|  | D) | energy |
|
|

