 |
| 1 |  | 
The plasma membrane is often described using the fluid-mosaic model. The term fluid describes the __________, and the __________ form a pattern, or a mosaic. |
|  | A) | glycoproteins; glycolipids |
|  | B) | glycolipids; glycoproteins |
|  | C) | protein molecules embedded in the membrane; double layer of phospholipids |
|  | D) | double layer of phospholipids; protein molecules embedded in the membrane |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Which choice correctly identifies the proteins?
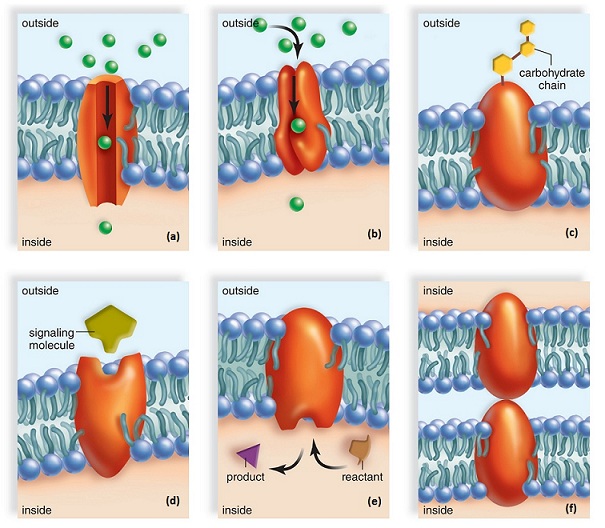 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028590/ch05Post_Q2_Q3_resized.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (167.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028590/ch05Post_Q2_Q3_resized.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (167.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | (a) carrier protein; (b) channel protein; (c) cell recognition protein; (d) receptor protein; (e) enzymatic protein; (f) junction protein |
|  | B) | (a) channel protein; (b) carrier protein; (c) cell recognition protein; (d) enzymatic protein; (e) receptor protein; (f) junction protein |
|  | C) | (a) carrier protein; (b) channel protein; (c) cell recognition protein; (d) enzymatic protein; (e) receptor protein; (f) junction protein |
|  | D) | (a) channel protein; (b) carrier protein; (c) cell recognition protein; (d) receptor protein; (e) enzymatic protein; (f) junction protein |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Which of these proteins is a glycoprotein?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028590/ch05Post_Q2_Q3_resized.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (167.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028590/ch05Post_Q2_Q3_resized.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (167.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | protein (3) |
|  | B) | protein (1) |
|  | C) | protein (4) |
|  | D) | protein (6) |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Which of the following is required for facilitated diffusion that is not required for simple diffusion? |
|  | A) | energy |
|  | B) | a transporter, such as a carrier or channel protein |
|  | C) | a concentration gradient |
|  | D) | a transporter, such as a junction protein |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
An animal cell placed in a hypotonic solution __________. A plant cell placed in a hypotonic solution _________. |
|  | A) | shrinks; is turgid |
|  | B) | is turgid; swells until it bursts |
|  | C) | swells until it bursts; is turgid |
|  | D) | is normal; is normal |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
An animal cell placed in a hypertonic solution __________. When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, _________. |
|  | A) | remains normal; turgor pressure increases |
|  | B) | remains normal; the cell bursts |
|  | C) | swells until it bursts; the cell is turgid |
|  | D) | shrinks; plasmolysis occurs |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Active transport requires __________ and moves things like sugars, amino acids, and ions. Bulk transport requires __________ and moves things like polypeptides, polysaccharides, and particles. |
|  | A) | a transporter and energy; vesicle formation |
|  | B) | vesicle formation; a transporter and energy |
|  | C) | energy; a transporter |
|  | D) | a channel protein; a carrier protein |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Plant cells are connected by __________, channels that pass through the cell wall. Materials can be exchanged between plant cells via these channels, specifically via cytoplasmic strands. |
|  | A) | tight junctions |
|  | B) | gap junctions |
|  | C) | anchoring junctions |
|  | D) | plasmodesmata |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Animal cells are connected by a few different kinds of junctions, depending on the type of tissue. Tissues that require leak-proof connections are composed of cells connected by _________ junctions. Tissues that stretch are composed of cells connected by _________ junctions. A _________ junction is formed when two identical plasma membrane channels join. These junctions lend strength to cells, but also allow materials to pass between them. |
|  | A) | gap; tight; anchoring |
|  | B) | tight; anchoring; gap |
|  | C) | tight; gap; anchoring |
|  | D) | anchoring; tight; gap |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Where junctions are not present, the space between animal cells is filled with a protein-rich __________ composed of proteins that include collagen and elastin. |
|  | A) | middle lamella |
|  | B) | cartilage |
|  | C) | extracellular matrix |
|  | D) | bone |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Energy is transformed from one form to another. It is acquired, stored, and released by living things. It is measured in calories, which are defined as __________. |
|  | A) | the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 100o C. |
|  | B) | the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 10 g of water by 1o K. |
|  | C) | the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1o C. |
|  | D) | the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1oC. |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, though it can be changed from one form to another. During the process of changing from one form to another, |
|  | A) | some energy is lost as heat, and is no longer usable to perform work. |
|  | B) | energy loses the ability to be changed back. |
|  | C) | some energy is lost as heat, but is still available to do work. |
|  | D) | some energy is gained as heat. |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
True or False: Energy cycles through living things. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
Why is a molecule of ATP well-suited to serve as an energy donor and not an energy storage molecule? |
|  | A) | ATP contains energy in its H-C bonds, whereas an energy storage molecule contains its energy in P-P bonds. |
|  | B) | ATP is a stable molecule that is difficult to break down. An energy storage molecule is unstable, so that harvesting the energy is relatively easy. |
|  | C) | ATP is an unstable molecule that readily breaks down at its P-P bonds to release energy. An energy storage molecule is stable, storing energy in its many H-C bonds. |
|  | D) | ATP is an unstable molecule that readily breaks down at its C-H bonds to release energy. An energy storage molecule is stable, storing energy in its many P-P bonds. |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
ATP is used in endergonic reactions. This is because |
|  | A) | these reactions have low energy of activation. |
|  | B) | these reactions do not require energy to occur. |
|  | C) | these reactions require an energy input to occur. |
|  | D) | these reactions have high energy of activation. |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
A(n) __________ reaction is used to build up ATP, which is then available to drive a(n) __________ reaction. |
|  | A) | endergonic; exergonic |
|  | B) | inefficient; efficient |
|  | C) | efficient; inefficient |
|  | D) | exergonic; endergonic |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
An enzyme is usually a protein that functions as a catalyst. This means that enzymes |
|  | A) | speed chemical reactions through their breakdown during the reaction. |
|  | B) | speed chemical reactions without being affected by the reaction. |
|  | C) | increase the energy of activation needed for a reaction to proceed. |
|  | D) | are converted to substrate during a reaction. |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
Which of the following situations would negatively influence enzyme speed? |
|  | A) | during a reaction, the pH is monitored closely to remain at optimal level |
|  | B) | the substrate concentration is increased |
|  | C) | zinc is added to the reaction |
|  | D) | a reaction is being carried out under very high temperatures |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
An enzyme inhibitor binds to the allosteric site of an enzyme. This is called __________ inhibition. |
|  | A) | competitive |
|  | B) | noncompetitive |
|  | C) | reversible |
|  | D) | permanent |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
The purpose of an enzyme inhibitor in a metabolic pathway is to decrease the activity of an enzyme once |
|  | A) | the substrate concentration is too high and the enzyme cannot speed the reaction any further. |
|  | B) | the enzyme gets close to running out. |
|  | C) | a reaction has produced sufficient product and a cell needs to conserve raw materials and energy. |
|  | D) | an enzyme’s shape has been altered so that is unable to combine efficiently with its substrate. |
|
|

