 |
| 1 |  | 
In the figure, a closeup of the chloroplast is included. Which structures of this organelle are identified by the numbers?
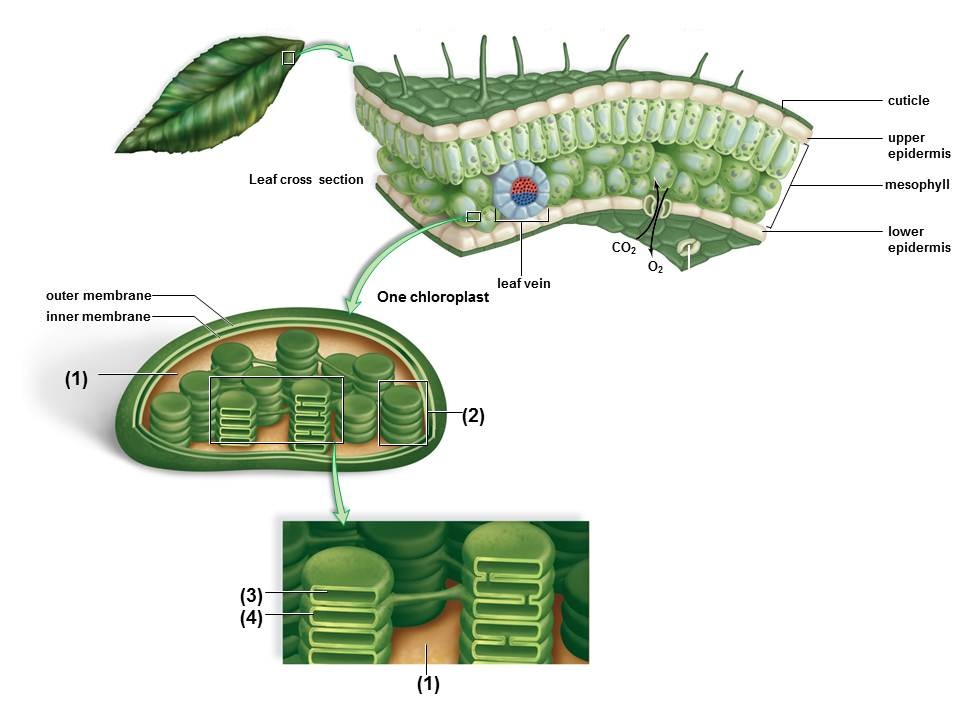 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch06Post_Q1_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (106.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch06Post_Q1_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (106.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | The numbers on the figure indicate the (1) grana, (2) stroma, (3) thylakoid membrane, and (4) thylakoid space. |
|  | B) | The numbers on the figure indicate the (1) thylakoid membrane, (2) thylakoids space, (3) stroma, and (4) grana. |
|  | C) | The numbers on the figure indicate the (1) stomata, (2) grana, (3) thylakoid space, and (4) thylakoid membrane. |
|  | D) | The numbers on the figure indicate the (1) stroma, (2) grana, (3) thylakoid space, and (4) thylakoid membrane. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
In the figure below, carbon dioxide and oxygen are shown entering and exiting the leaf through which of the following structures?
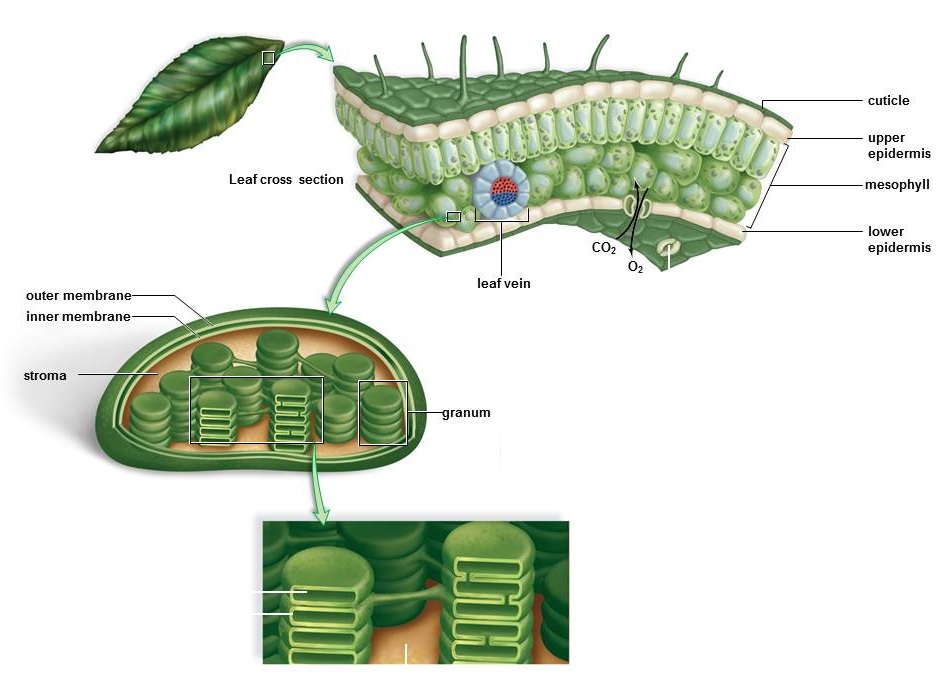 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch06Post_Q2_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (118.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch06Post_Q2_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (118.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | stomata (sing., stoma) |
|  | B) | grana (sing., granum) |
|  | C) | stroma |
|  | D) | thylakoids |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
How do the raw materials for photosynthesis enter a plant and reach the chloroplasts? |
|  | A) | Stomata in the leaves allow water in; carbon dioxide diffuses into the roots. These materials then diffuse into the chloroplasts. |
|  | B) | The roots absorb carbon dioxide; water enters through stomata in the leaves. The materials are carried by bulk transport into the chloroplasts. |
|  | C) | The roots absorb water; carbon dioxide enters through stomata in the leaves. These materials are then carried by active transport into the chloroplasts. |
|  | D) | The roots absorb water; carbon dioxide enters through stomata in the leaves. These materials then diffuse into the chloroplasts. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Photosynthesis is sometimes called a redox reaction because |
|  | A) | the terms “reduction” and “reaction” are shortened to “redox”. |
|  | B) | oxidation and reduction both occur during this reaction: water is oxidized and carbon dioxide is reduced. The “red” in reduction is combined with the “ox” in oxidation, shortened to “redox”. |
|  | C) | redox means that two sets of reactions occur: the light reactions and the Calvin cycle. |
|  | D) | reduction occurs first, then oxidation; otherwise, it would be called an redox reaction. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Two sets of reactions take place within the process of photosynthesis. How does one set of reactions influence the other? |
|  | A) | Products of the light reaction (NADP+ and ADP + P) enter the Calvin cycle; products of the Calvin cycle (NADPH and ATP) are sent back to the light reactions. |
|  | B) | There is no influence. Each set of reactions occurs separately and they have nothing in common. |
|  | C) | Products of the light reaction (NADPH and ATP) enter the Calvin cycle; products of the Calvin cycle (NADP+ and ADP + P) are sent back to the light reactions. |
|  | D) | The raw materials (reactants) of the light reactions (H2O) are reused in the Calvin cycle. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Photosynthetic pigments absorb solar energy. Different wavelengths of this light are absorbed by different pigments; the absorption spectrums of three photosynthetic pigments are shown below. Chlorophyll a and b absorb ____________ light better than other colors; this is why leaves appear green. Carotenoids absorb __________ and reflect yellow or orange.
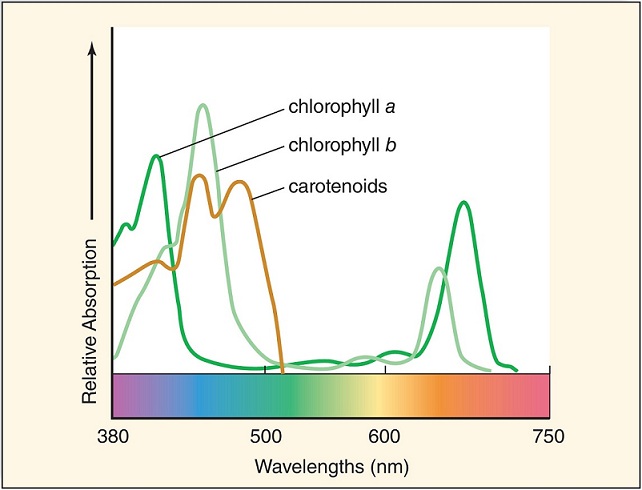 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028591/ch06Post_Q6_resized.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (85.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028591/ch06Post_Q6_resized.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (85.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | violet, blue, and red; yellow, orange, and red |
|  | B) | green; violet, blue, and green |
|  | C) | violet, blue, and green; violet, blue, and red |
|  | D) | violet, blue, and red; violet, blue, and green |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
A photosystem has two parts: a(n) __________ that absorbs solar energy, and a(n) __________ molecule that receives excited electrons and passes them to the carriers of the electron transport chain. |
|  | A) | pigment complex; electron acceptor molecule |
|  | B) | reaction center; antenna molecule |
|  | C) | electron acceptor molecule; pigment complex |
|  | D) | antenna molecule; reaction center |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
How is solar energy captured and transformed to a form that is usable in photosynthesis? |
|  | A) | Solar energy is first absorbed by the electron transport chain and then converted into ATP by pigments. |
|  | B) | Solar energy is first absorbed by pigments in the stroma and then converted into glucose in the electron transport chain. |
|  | C) | Solar energy is first absorbed by pigments in the thylakoids, and then converted to ATP in the electron transport chain. |
|  | D) | Solar energy is first absorbed by the stomata of a leaf and is then converted to glucose in the Calvin cycle. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
During the light reactions, solar energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of ATP. This happens because as electrons move down the electron transport chain, hydrogen ions (H+) are pumped outside the thylakoid membrane. A hydrogen __________ is established across the thylakoid membrane, providing the basis for the flow of H+ through the channels of ATP synthase complexes. The complexes use the kinetic energy that results from the ion flow to produce ATP from ADP + P. This process is called __________. |
|  | A) | pump; reduction |
|  | B) | gradient; chemiosmosis |
|  | C) | gradient; oxidation |
|  | D) | pump; chemiosmosis |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
During the light reactions, electrons move along a __________ pathway, moving from __________ to NADP+. Oxygen is released and ATP is produced. |
|  | A) | noncyclic; carbon dioxide |
|  | B) | cyclic; carbon dioxide |
|  | C) | noncyclic; water |
|  | D) | cyclic; water |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Excited electrons move from the electron acceptor in __________ to the electron transport chain. Excited electrons move from the electron acceptor in __________ to reduce NADP+ to NADPH. |
|  | A) | photosystem I; photosystem II |
|  | B) | the thylakoid membrane; the stroma |
|  | C) | the stroma; the thylakoid |
|  | D) | photosystem II; photosystem I |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
If the molecular complexes of the thylakoid are divided into two categories: those that “get ready”, making preparations for the production of the materials needed for the Calvin cycle, and those that “payoff”, or actually produce the materials needed for the Calvin cycle, which complexes belong to the first category and which belong to the second? |
|  | A) | Get ready: photosystem II, electron transport chain, photosystem I; Payoff: NADP+ reductase, the H+ gradient and the ATP synthase complex |
|  | B) | Get ready: NADP+ reductase, the H+ gradient and the ATP synthase; Payoff: photosystem II, electron transport chain, photosystem I complex |
|  | C) | Get ready: photosystem II, photosystem I; Payoff: electron transport chain, NADP+ reductase, the H+ gradient and the ATP synthase complex |
|  | D) | Get ready: NADP+ reductase, the H+ gradient and the ATP synthase complex; Payoff: photosystem II, photosystem I, electron transport chain |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
During the first stage of the Calvin cycle, called the ________ stage, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere combines with RuBP to form a 6-carbon molecule which __________. |
|  | A) | glycolysis; breaks down to release oxygen and hydrogen ions |
|  | B) | regeneration of RuBP; immediately splits into two molecules of 3PG |
|  | C) | CO2 reduction; breaks down into two molecules of BPG |
|  | D) | CO2 fixation; immediately splits to form two molecules of 3PG |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
Why is there so much RuBP carboxylase in the chloroplasts? |
|  | A) | because there is so much CO2 coming in to be turned into sugar |
|  | B) | because this enzyme is very slow, so there has to be a lot of it to keep the cycle going |
|  | C) | because this protein is also a major component of the grana |
|  | D) | because it is the only enzyme involved in photosynthesis |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
During the second stage of the Calvin cycle, called the ________ stage, each of the 3-carbon intermediates resulting from stage one is __________ using ATP and NADPH produced by the light reactions. This step sends some ADP+P and NADP+ back to the light reactions. |
|  | A) | glycolysis; reduced to BPG in two steps |
|  | B) | regeneration of RuBP; oxidized to G3P in a single step |
|  | C) | CO2 reduction; reduced to G3P in two steps |
|  | D) | CO2 oxidation; oxidized to G3p in two steps |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
The final stage of the Calvin cycle, regeneration of RuBP, takes care of replenishing the protein RuBP. ATP from the light reactions helps this process along. For each of the three turns of the cycle required to release one molecule of G3P, __________ G3P molecules are used to reform __________ molecules of RuBP, and the cycle continues. This reaction also sends some ADP+P and NADP+ back to the light reactions. |
|  | A) | two; six |
|  | B) | six; two |
|  | C) | three; five |
|  | D) | five; three |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
Use the figure to help you complete the following statements:
To form glucose, __________ molecules of carbon dioxide must enter the Calvin cycle. This requires __________ ATP and __________ NADPH produced from the light reactions.
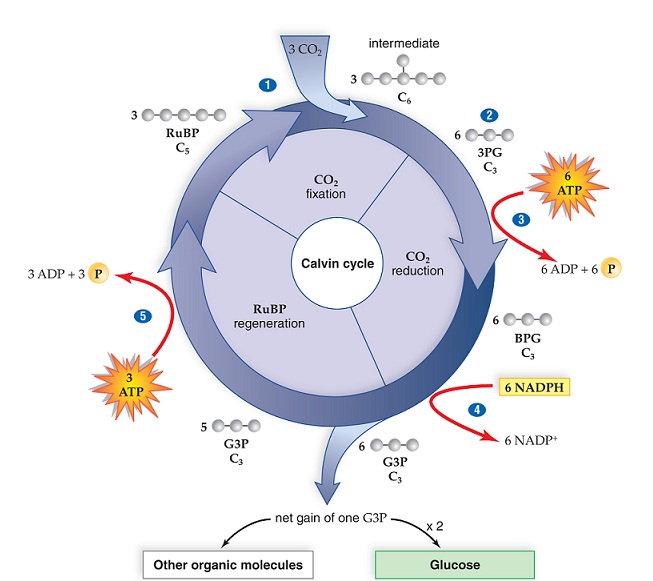 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch06Post_Q17_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (122.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch06Post_Q17_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (122.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | 6; 18; 12 |
|  | B) | 3; 9; 6 |
|  | C) | 1; 3; 2 |
|  | D) | 9; 27; 18 |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
What differences would you expect to see in the leaves of a C4 plant that you would not see in a C3 or CAM plant? |
|  | A) | mesophyll cells arranged in parallel rows |
|  | B) | each leaf vein at the center of a circle of mesophyll cells, which are surrounded by a concentric circle of bundle sheath cells |
|  | C) | random arrangement of mesophyll cells |
|  | D) | each leaf vein at the center of a circle of bundle sheath cells, which is surrounded by a concentric circle of mesophyll cells |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
C3 plants are better-suited than C4 plants for cool, moist weather. However, C3 photosynthesis does have a drawback: __________. C4 photosynthesis is better-suited than C3 photosynthesis for hot, dry weather, but it __________ to make C4 molecules. It is worth it, if the weather is hot and dry, however. |
|  | A) | it is energetically expensive; is limited by CO2 availability |
|  | B) | photorespiration; it is energetically expensive |
|  | C) | it is energetically expensive; can be limited by high levels of O2 |
|  | D) | it is limited by CO2 availability; it is energetically expensive |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
CAM photosynthesis, like C4 photosynthesis, separates the light reactions and the Calvin cycle. The difference is, instead of separating them ________ like C4 photosynthesis, CAM photosynthesis separates them __________. This can be beneficial in a hot, dry place like the desert because it conserves water. |
|  | A) | depending on temperature; depending on precipitation |
|  | B) | in time; in space |
|  | C) | in space; in time |
|  | D) | depending on precipitation; depending on temperature |
|
|

