 |
| 1 |  | 
During the process of cellular respiration, __________ is oxidized and __________ is reduced. As you may recall from the discussion of photosynthesis in chapter 6, when oxidation and reduction take place in an overall reaction, the reaction is referred to as a __________ reaction. |
|  | A) | glucose; oxygen; hydrolysis |
|  | B) | oxygen; glucose; synthesis |
|  | C) | carbon dioxide; water; redox |
|  | D) | glucose; oxygen; redox |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
NAD+ and FAD are __________ involved in the oxidation of the products formed when glucose is broken down; these molecules __________ electrons and hydrogen ions. |
|  | A) | coenzymes; accept |
|  | B) | coenzymes; donate |
|  | C) | substrates; accept |
|  | D) | substrates; donate |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
The first phase of cellular respiration, __________, occurs in the __________ of a cell. This stage breaks glucose down into two molecules of pyruvate; it produces NADH and 2 molecules of ATP. |
|  | A) | the preparatory reaction; cytoplasm |
|  | B) | glycolysis; mitochondrial matrix |
|  | C) | the preparatory reaction; mitochondrial matrix |
|  | D) | glycolysis; cytoplasm |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
The second phase of cellular respiration, __________, occurs in the mitochondrial matrix; in this stage, NADH is formed and __________ is released as pyruvate is broken down. |
|  | A) | the Krebs cycle; H2O |
|  | B) | the preparatory reaction; CO2 |
|  | C) | glycolysis; O2 |
|  | D) | the Calvin cycle; CO2 |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
The third phase of cellular respiration, __________, takes place in the __________; in this stage, CO2 is released, NADH and FADH2 are formed, and 2 ATP molecules are produced for each molecule of glucose. |
|  | A) | the preparatory reaction; mitochondrial matrix |
|  | B) | glycolysis; cytoplasm |
|  | C) | the Krebs cycle; mitochondrial matrix |
|  | D) | the Krebs cycle; mitochondrial cristae |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
The final phase of cellular respiration involves an electron transport chain and chemiosmosis; this stage takes place in the __________ and produces the __________ amount of ATP during the entire process. |
|  | A) | cytoplasm of the cell; smallest |
|  | B) | mitochondrial matrix; greatest |
|  | C) | mitochondrial cristae; smallest |
|  | D) | mitochondrial cristae; greatest |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
The inputs of glycolysis are __________ and the outputs are __________. |
|  | A) | 2 ATP, glucose, and 2 NAD+; 2 (net) ATP, 2 pyruvate, and 2 NADH |
|  | B) | 2 (net) ATP, 2 pyruvate, and 2 NADH; 2 ATP, glucose, and 2 NAD+ |
|  | C) | 2 ATP, glucose, NAD+ and FAD; 4 (net) ATP, 2 pyruvate, 2 NADH and FADH2 |
|  | D) | 4 ATP, 2 glucose, NAD+ and FAD; 2 (net) ATP, 2 pyruvate, 2 NADH and FADH2 |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
This figure depicts __________. The molecule colored blue and indicated with the “a” is an __________.
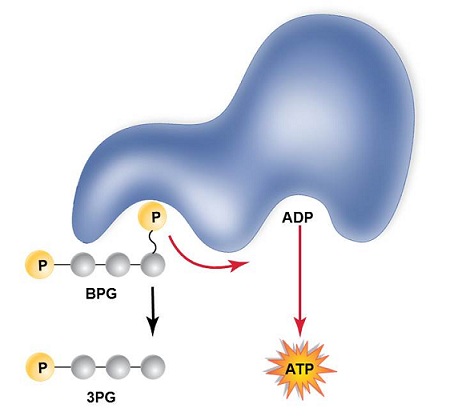 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch07Post_Q7_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (29.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch07Post_Q7_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (29.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | chemiosmosis; enzyme |
|  | B) | substrate-level ATP synthesis; ATP synthase complex |
|  | C) | chemiosmosis; ATP synthase complex |
|  | D) | substrate-level ATP synthesis; enzyme |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Splitting glucose into 2 G3P molecules is often called an __________ step because it __________. |
|  | A) | energy-harvesting; produces 4 ATP, or a net 2 ATP |
|  | B) | energy-investment; requires 2 ATP, or an energy input |
|  | C) | energy-harvesting; requires 2 ATP, or an energy output |
|  | D) | energy-investment; produces 4 ATP, or a net 2 ATP |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Oxidizing G3P, two rounds of substrate-level ATP synthesis, and oxidation of 3PG to end up with 2 pyruvate molecules are all __________ steps during glycolysis because _________. |
|  | A) | energy-harvesting; 2 ATP are required, which is an energy input |
|  | B) | energy-investment; 4 ATP are produced, or a net of 2 ATP |
|  | C) | energy-harvesting; 4 ATP are produced, or a net of 2 ATP |
|  | D) | energy-investment; 2 ATP are required, which is an energy input |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Which product(s) of the preparatory (prep) reaction go on to enter the Krebs cycle? |
|  | A) | All of these products go on to enter the Krebs cycle. |
|  | B) | 2 NADH |
|  | C) | 2 CO2 |
|  | D) | 2 acetyl~CoA |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
The Krebs cycle turns __________ for each original glucose molecule. Following the complete breakdown of glucose, several separate oxidation reactions will result in a total of__________ NADH and __________ FADH2. Four molecules of carbon dioxide are released as a result of the first two oxidation reactions, and, via substrate-level synthesis, 2 molecules of ATP also result. |
|  | A) | twice; six; two |
|  | B) | three times; nine; three |
|  | C) | twice; two; six |
|  | D) | three times; three; nine |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
High-energy electrons are delivered to the electron transport chain, a series of electron carriers in the cristae of the mitochondrion. These electrons are carried by __________ that have formed during __________. |
|  | A) | NADH and FADH2; photosynthesis |
|  | B) | NAD+ and FAD; glycolysis, the preparatory reaction, and the Krebs cycle |
|  | C) | NAD+ and FAD; photosynthesis |
|  | D) | NADH and FADH2; glycolysis, the preparatory reaction, and the Krebs cycle |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
__________ ATP are produced per glucose molecule in the mitochondrial cristae, specifically in the series of electron carriers embedded in the membrane. __________ is the final electron acceptor in this chain, and as ATP are produced, this molecule combines with hydrogen ions to form water. |
|  | A) | 36 or 38; carbon dioxide |
|  | B) | 32 or 34; oxygen |
|  | C) | 32 or 34; carbon dioxide |
|  | D) | 36 or 38; oxygen |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
As in photosynthesis, the electron transport chain of cellular respiration results in the production of ATP as high-energy electrons are passed along a series of carrier molecules in a membrane. This movement is not entirely responsible for the production of ATP, though. As the electrons move, what happens to the hydrogen ions carried by FADH2 and NADH? What ATP-producing process follows? |
|  | A) | The H+ is picked up by free NAD+ and FAD in the cytoplasm. Substrate-level ATP synthesis produces ATP as an enzyme passes a high-energy phosphate to ADP. |
|  | B) | The H+ is pumped into the intermembrane space. Substrate-level ATP synthesis produces ATP as an enzyme passes a high-energy phosphate to ADP. |
|  | C) | The H+ is pumped into the intermembrane space. Chemiosomosis produces ATP as the H+ gradient fuels the enzyme ATP synthase, which synthesizes ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. |
|  | D) | The H+ is picked up by free NAD+ and FAD+ in the cytoplasm. Chemiosomosis produces ATP as the H+ gradient fuels the enzyme ATP synthase, which synthesizes ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
The ATP payoff of cellular respiration can be calculated if the number of ATP that are used in the process are subtracted from the total number produced. Which step does not directly generate ATP, and how many net ATP are produced by the overall process of cellular respiration? |
|  | A) | the electron transport chain; 32 or 34 net ATP |
|  | B) | glycolysis; 32 or 34 net ATP |
|  | C) | the Krebs cycle; 36 or 38 net ATP |
|  | D) | the preparatory reaction; 36 or 38 net ATP |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
Substrate-level ATP synthesis accounts for __________ and chemiosmosis accounts for __________ of the ATP produced during cellular respiration. |
|  | A) | 4; 32 or 34 |
|  | B) | 2; 34 or 36 |
|  | C) | 4; 36 or 38 |
|  | D) | 2: 36 or 38 |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
Both glycolysis and fermentation produce __________ oxygen; however, if fermentation occurs, the NADH produced by glycolysis __________. |
|  | A) | 2 ATP in the presence of; move to the cristae to give up high-energy electrons to the carrier molecules of the ETC |
|  | B) | 2 ATP in the absence of; move to the cristae to give up high-energy electrons to the carrier molecules of the ETC |
|  | C) | 2 ATP in the presence of; does not move to the ETC, but instead becomes NAD+ again after giving its electrons to pyruvate. |
|  | D) | 2 ATP in the absence of; does not move to the ETC, but instead becomes NAD+ again after giving its electrons to pyruvate. |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
The products of fermentation are __________; this process is important for ATP production during activities like __________. |
|  | A) | harmless; vigorous exercise |
|  | B) | toxic to cells; vigorous exercise |
|  | C) | harmless; deep breathing exercises |
|  | D) | toxic to cells; deep breathing exercises |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
Which of the following best explains how catabolic reactions, like breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, or fats, drive synthesis reactions? |
|  | A) | Catabolic reactions release energy that can be used for anabolic pathways. |
|  | B) | Catabolic reactions provide raw materials for synthesis and release energy that can be used for anabolic pathways. |
|  | C) | Catabolic reactions provide raw materials for synthesis. |
|  | D) | The products of catabolic reactions can be converted to amino acids via transamination. |
|
|

