 |
| 1 |  | 
The members of an autosome chromosome pair, called __________, look alike and carry genes for the same traits; __________ occur at the same location on each pair. |
|  | A) | non-sister chromatids; homologues |
|  | B) | sister chromatids; alleles |
|  | C) | alleles; homologues |
|  | D) | homologues; alleles |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
In humans there are 22 pairs of chromosomes, called __________, which replicate via mitosis; one pair of chromosomes, called __________, are produced via meiosis. |
|  | A) | homologous chromosomes; non-sister chromatids |
|  | B) | x chromosomes; y chromosomes |
|  | C) | sex chromosomes; autosomes |
|  | D) | autosomes; sex chromosomes |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
In humans, __________ determine the gender of individuals. The presence of __________ chromosome(s) is characteristic of a female; __________ chromosome(s) is characteristic of a male. |
|  | A) | autosomes; an X; a Y |
|  | B) | sex chromosomes; two X; two Y |
|  | C) | autosomes; two X; one X and one Y |
|  | D) | sex chromosomes; two X; one X and one Y |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Synapsis plays a large role in the reduction division that is meiosis. How does this process help reduce chromosome number? |
|  | A) | It permits the orderly separation of homologues by lining up the pairs of homologous chromosomes during meiosis II. |
|  | B) | It permits the orderly separation of homologues by lining up the pairs of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I. |
|  | C) | It permits the orderly separation of homologues by lining up the pairs of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and II. |
|  | D) | It permits the exchange of genetic information between non-sister chromatids. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Between meiosis I and II __________ during a period of time called __________. |
|  | A) | DNA is not replicated; cytokinesis |
|  | B) | DNA replicates in preparation for another division; interkinesis |
|  | C) | DNA is not replicated; interkinesis |
|  | D) | DNA replicates in preparation for another division; cytokinesis |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Which two processes are depicted in the figure?
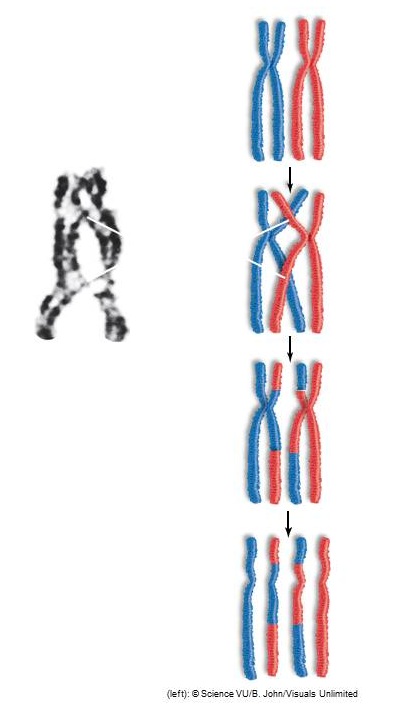 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch09Post_Q6_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (45.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch09Post_Q6_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (45.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | mitosis and nondisjunction |
|  | B) | synapsis and independent assortment |
|  | C) | nondisjunction and crossing-over |
|  | D) | synapsis and crossing-over |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Homologues carry alleles for the same traits. During the initial stages of synapsis, only __________ chromatids can carry different genetic information. After crossing-over occurs between homologues, the __________ chromatids carry different genetic information, demonstrated by the different colors in the figure.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch09Post_Q6_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (45.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073525537/1028583/ch09Post_Q6_ref.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (45.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | nonsister; sister |
|  | B) | sister; sister |
|  | C) | daughter; sister |
|  | D) | sister; daughter |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
What is the effect of crossing-over on the daughter chromosomes, those chromosomes that result once sister chromatids are separated by the first division of meiosis? |
|  | A) | Crossing-over deletes some alleles and duplicates others so the daughter chromosomes contain the new mutations. |
|  | B) | Crossing-over does not have any detectable effect on the daughter chromosomes. |
|  | C) | Through crossing-over and the first division of meiosis, four genetically identical daughter chromosomes result. |
|  | D) | Through crossing-over and the first division of meiosis, four genetically different, or recombinant, daughter chromosomes result. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Which phenomenon, along with crossing-over, increases genetic variation during the formation of gametes? |
|  | A) | synapsis |
|  | B) | independent assortment |
|  | C) | interkinesis |
|  | D) | cytokinesis |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Meiosis occurs in two parts, each with same four phases that occur during mitosis. Meiosis I is a bit different than mitosis, in that |
|  | A) | a spindle apparatus forms to separate chromosomes. |
|  | B) | chromosomes duplicate before the cells divide. |
|  | C) | synapsis occurs during meiosis I and genetic variation is introduced through crossing-over and independent assortment during meiosis I. |
|  | D) | the cells are haploid (n = 2). |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
What happens during the first half of meiosis? During __________ of homologues pair during synapsis, during ___________ homologues randomly align at the equator, and during __________ homologues separate. |
|  | A) | prophase I, anaphase I, telophase I |
|  | B) | anaphase I, metaphase I, telophase I |
|  | C) | anaphase I, metaphase I, interkinesis |
|  | D) | prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
The second half of meiosis, meiosis II, takes place after a period called interkinesis. At the beginning of prophase I, __________. The chromosomes __________ during metaphase II, and separate during anaphase II to become daughter chromosomes. |
|  | A) | nondisjunction occurs; align at the equator |
|  | B) | crossing-over occurs; synapse |
|  | C) | tetrads form and synapsis occurs; cross-over |
|  | D) | cells have one chromosome from each homologue; align at the equator |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
Meiosis occurs in two parts, each with same four phases that occur during mitosis. Meiosis II essentially only differs from mitosis in that |
|  | A) | the cells are haploid. |
|  | B) | a spindle appears during prophase II. |
|  | C) | sister chromatids are separated. |
|  | D) | chromosomes line up at the equator during metaphase II. |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
When the nuclear envelopes reform during __________, each nucleus is haploid. |
|  | A) | telophase I |
|  | B) | telophase I and telophase II |
|  | C) | telophase II |
|  | D) | interkinesis |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
During meiosis, a 2n parent cell divides to form |
|  | A) | two n daughter nuclei. |
|  | B) | one 2n daughter nucleus. |
|  | C) | four n daughter nuclei. |
|  | D) | two 2n daughter nuclei. |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
The events of meiosis II are nearly identical to mitosis, aside from |
|  | A) | the diploid chromosome number of the daughter cells in meiosis II. |
|  | B) | the haploid chromosome number of the daughter cells in meiosis II. |
|  | C) | the fact that meiosis II produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. |
|  | D) | the fact that mitosis produces daughter cells that are genetically dissimilar to each other and to the parent cell. |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
Mitosis requires _____, while meiosis requires _____. |
|  | A) | one nuclear division; two nuclear divisions |
|  | B) | two nuclear divisions; one nuclear division |
|  | C) | one nuclear replication; two nuclear replications |
|  | D) | two nuclear replications; one nuclear replication |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
If a eukaryote has three or more complete sets of chromosomes, it is called __________. An individual with a chromosome number that is not an exact multiple of the haploid number for the species is __________. |
|  | A) | a polyploid; an aneuploid |
|  | B) | a triploid; a polyploid |
|  | C) | an aneuploid; a polyploid |
|  | D) | trisomatic; an aneuploid |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
Chromosomal abnormalities are usually caused by nondisjunction, which can occur during meiosis I, if __________, or during meiosis II, if __________. It will result in aneuploidy if one of these gametes fuses with a normal gamete and development continues. |
|  | A) | sister chromatids fail to separate and both daughter chromosomes go into the same gamete; homologues fail to separate and both go into the same gamete |
|  | B) | homologues fail to separate and both go into the same gamete; sister chromatids fail to separate and both daughter chromosomes go into the same gamete |
|  | C) | the homologues do not come together during synapsis; the chromosomes do not independently assort |
|  | D) | the chromosomes do not independently assort; the homologues do not come together during synapsis |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
The chapter discusses Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome, all of which are due to differences in chromosome number like trisomy and sex chromosome anomalies. What characteristics are associated with these syndromes? |
|  | A) | Down syndrome: underdeveloped testes and prostate, lack of facial hair, large hands and feet with long limbs; Turner syndrome: short stature, broad chest, neck webbing; Klinefelter syndrome: short stature, flat face, intellectual disability, and a large, fissured tongue |
|  | B) | Down syndrome: short stature, broad chest, neck webbing; Turner syndrome: short stature, flat face, intellectual disability, and a large, fissured tongue; Klinefelter syndrome: underdeveloped testes and prostate, lack of facial hair, large hands and feet with long limbs |
|  | C) | Down syndrome: short stature, flat face, intellectual disability, and a large, fissured tongue; Turner syndrome: short stature, broad chest, neck webbing; Klinefelter syndrome: underdeveloped testes and prostate, lack of facial hair, large hands and feet with long limbs |
|  | D) | Down syndrome: short stature, flat face, intellectual disability, and a large, fissured tongue; Turner syndrome: underdeveloped testes and prostate, lack of facial hair, large hands and feet with long limbs; Klinefelter syndrome: short stature, broad chest, neck webbing |
|
|

