 |
1 |  | 
Which of the following is not a reason for using a model? |
|  | A) | A model is quicker and easier to build than the real thing |
|  | B) | We can use a model in simulations to test our ideas |
|  | C) | We can use a model instead of building the real thing |
 |
 |
2 |  | 
Which of the following is not a model? |
|  | A) | An Airbus 380. |
|  | B) | A scale model of an Airbus 380 to use in a wind tunnel. |
|  | C) | An engineer’s drawing of a cross-section through the fuselage of an Airbus 380. |
 |
 |
3 |  | 
Analysts and designers use models that consist of which of the following? |
|  | A) | Diagrams and text |
|  | B) | Only diagrams |
|  | C) | Only text |
 |
 |
4 |  | 
Which of the following do analysts and designers use diagrams for? |
|  | A) | To communicate ideas |
|  | B) | To understand structures and relationships |
|  | C) | Both 1 and 2 |
 |
 |
5 |  | 
Which of the following do analysts and designers use diagrams for? |
|  | A) | To ensure that users don’t understand the specification for a system |
|  | B) | To communicate ideas to users and other analysts and designers |
|  | C) | Neither A nor B |
 |
 |
6 |  | 
Why are systems analysis and design diagram standards important? |
|  | A) | They promote communication between team members |
|  | B) | They provide work for international standards committees |
|  | C) | They prevent systems analysts’ clothes from shrinking in the wash |
 |
 |
7 |  | 
Which of the following are the rules that modelling techniques should enforce? |
|  | A) | Simplicity of representation, external consistency, completeness and network representation |
|  | B) | Simplicity of representation, internal consistency, completeness and hierarchical representation |
|  | C) | Simplicity, internal consistency, completeness and hierarchical symbols |
 |
 |
8 |  | 
Which of the following is true? |
|  | A) | Icons can contain two-dimensional symbols |
|  | B) | Two-dimensional symbols can contain icons |
|  | C) | An icon contains at least one vertex and one string |
 |
 |
9 |  | 
Which of the following is true? |
|  | A) | A model consists of one and only one diagram |
|  | B) | A diagram contains at least one model |
|  | C) | A model contains diagrams |
 |
 |
10 |  | 
Which of the following is the UML notation for a model? |
|  | A) |  <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::Answer A::/sites/dl/free/0077110005/41598/mcq_ch05_11a.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Answer A (0.0K)</a>Answer A <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::Answer A::/sites/dl/free/0077110005/41598/mcq_ch05_11a.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Answer A (0.0K)</a>Answer A |
|  | B) |  <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::Answer B::/sites/dl/free/0077110005/41598/mcq_ch05_11b.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Answer B (0.0K)</a>Answer B <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::Answer B::/sites/dl/free/0077110005/41598/mcq_ch05_11b.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Answer B (0.0K)</a>Answer B |
|  | C) | 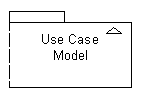 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::Answer C::/sites/dl/free/0077110005/41598/mcq_ch05_11c.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Answer C (0.0K)</a>Answer C <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::Answer C::/sites/dl/free/0077110005/41598/mcq_ch05_11c.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Answer C (0.0K)</a>Answer C |
 |
 |
11 |  | 
Which of the following does the Figure below show?  <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::Image::/sites/dl/free/0077110005/41598/mcq_ch05_12.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Image (0.0K)</a>Image <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::Image::/sites/dl/free/0077110005/41598/mcq_ch05_12.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Image (0.0K)</a>Image
|
|  | A) | A model. |
|  | B) | A sub-system |
|  | C) | A package |
 |
 |
12 |  | 
As a model is developed it, which of the following does it become? |
|  | A) | More abstract |
|  | B) | More detailed |
|  | C) | Less formal |
 |
 |
13 |  | 
Which of the following is not a purpose for using activity diagrams? |
|  | A) | To show the sub-systems that make up a system |
|  | B) | To model a task |
|  | C) | To describe the logic of an operation |
 |
 |
14 |  | 
Which of the following does the figure below show? 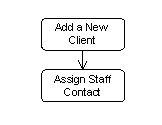 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::Image::/sites/dl/free/0077110005/315092/51.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Image (7.0K)</a>Image <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::Image::/sites/dl/free/0077110005/315092/51.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Image (7.0K)</a>Image
|
|  | A) | Two actions joined by a control flow. |
|  | B) | Two control flows joined by an activity. |
|  | C) | Two actors joined by a control flow. |
 |
 |
15 |  | 
A decision node in an activity diagram is represented by which of the following? |
|  | A) | A black circle in a white circle with a black border. |
|  | B) | A diamond. |
|  | C) | A rectangle. |
 |
 |
16 |  | 
Which of the following is shown by a statement in square brackets such as ‘[no staff to assign]’ alongside a control flow? |
|  | A) | An activity. |
|  | B) | An event. |
|  | C) | A guard condition. |
 |
 |
17 |  | 
What is shown by the arrows from the rectangles in the following diagram? 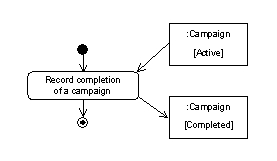 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::Image::/sites/dl/free/0077110005/315092/52.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Image (13.0K)</a>Image <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::Image::/sites/dl/free/0077110005/315092/52.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">Image (13.0K)</a>Image
|
|  | A) | Object flows. |
|  | B) | Data stores. |
|  | C) | Classes. |
 |
 |
18 |  | 
Which of the following is the name given to the division of an activity diagram into columns that represent where activities take place? |
|  | A) | Tracks. |
|  | B) | Activity zones. |
|  | C) | Activity partitions. |
 |
 |
19 |  | 
How many phases are there in the Unified Software Development Process? |
|  | A) | Three. |
|  | B) | Four. |
|  | C) | Five. |
 |
 |
20 |  | 
Which of the following are the phases of the Unified Software Development Process? |
|  | A) | Inception, elaboration, implementation, test. |
|  | B) | Analysis, design, implementation, test. |
|  | C) | Inception, elaboration, construction, transition. |
 |
 |
21 |  | 
Which of the following is a definition of a workflow in the Unified Software Development Process? |
|  | A) | A series of activities to be carried out and the roles of the people who will carry out those activities. |
|  | B) | A series of stages and the techniques that will be used in those stages. |
|  | C) | A series of products and the roles of the people who will produce those products. |
 |

