 |
| 1 |  | 
The cash account is affected by the |
|  | A) | Revenue cycle. |
|  | B) | Financing cycle. |
|  | C) | Purchasing cycle. |
|  | D) | All of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Comparing the dates for a sample of cheques with the dates the cheques cleared the bank is used to test |
|  | A) | Existence. |
|  | B) | Cut-off. |
|  | C) | Accuracy. |
|  | D) | Authorization. |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Tracing a sample of entries in the cash receipts journal to daily deposit slips tests which of the following assertions for cash? |
|  | A) | Occurrence. |
|  | B) | Completeness. |
|  | C) | Valuation. |
|  | D) | Cut-off. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
The auditor is most concerned with which management assertion during the audit of cash |
|  | A) | Valuation and Allocation. |
|  | B) | Rights and Obligations. |
|  | C) | Existence. |
|  | D) | Presentation and Disclosure. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Kiting can best be defined as a situation in which |
|  | A) | An entity employee is diverting deposits to his personal bank account. |
|  | B) | The entity fails to complete bank reconciliations on a timely basis. |
|  | C) | An employee fraudulently covers a cash shortage by transferring money from one bank account to another. |
|  | D) | Entity cheques include unauthorized signatures. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
On 31/12/13, Hoover Co. erroneously credited accounts payable (Dr. Cash; Cr. Accounts Payable) for a transfer of funds between two bank accounts that resulted in an overstatement of both cash and accounts payable at year-end. The cheque was not recorded until it cleared the bank on 2/1/14. Which of the following procedures would be least effective in detecting this misstatement? |
|  | A) | Review of the 31/12/13 bank reconciliations for the 2 bank accounts. |
|  | B) | Review of the schedule of interbank transfers. |
|  | C) | Review of the accounts payable supporting documentation at 31/12/13. |
|  | D) | Review of the December cheque register for both accounts. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Which of the following best explains why an auditor obtains a bank cut-off statement in connection with his/her examination of year-end cash balances? |
|  | A) | It is the best available procedure to detect kiting. |
|  | B) | Entities with poor liquidity may be likely to alter the year-end bank statement amounts. |
|  | C) | It assists in verifying deposits in transit and outstanding cheques from the year-end bank reconciliation on a timely basis. |
|  | D) | It is required per auditing standards if the auditor is unable to prepare a bank transfer schedule. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
An auditor ordinarily sends a confirmation request to all banks with which the entity has done business during the year under audit, regardless of the year-end balance. One purpose of this procedure is to |
|  | A) | Provide the data necessary to prepare a proof of cash. |
|  | B) | Request that a cut-off bank statement and related cheques be sent to the auditor. |
|  | C) | Detect kiting activities that may otherwise not be discovered. |
|  | D) | Seek information about loans from the banks. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
The primary evidence regarding year-end bank balances is documented in the |
|  | A) | Bank confirmations. |
|  | B) | Outstanding cheque listing. |
|  | C) | Interbank transfer schedule. |
|  | D) | Bank deposit lead schedule. |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
On receiving the cut-off bank statement, the auditor should vouch |
|  | A) | Deposits in transit on the year-end bank reconciliation to deposits in the cash receipts journal. |
|  | B) | Cheques dated before year-end listed as outstanding on the year-end bank reconciliation to the cut-off statement. |
|  | C) | Deposits listed on the cut-off statement to deposits in the cash receipts journal. |
|  | D) | Cheques dated after year-end to outstanding cheques listed on the year-end bank reconciliation and to the cut-off statement. |
|
|
 |
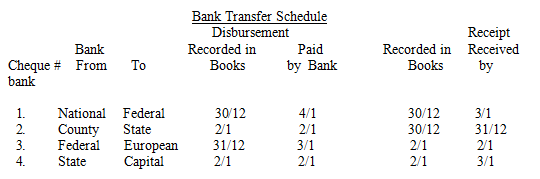
| 11 |  | 
The following information was taken from the bank transfer schedule prepared for the audit of Salt Fork Co. Assume all cheques were actually dated and mailed on 30/12.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=png::::/sites/dl/free/0077143019/1013351/ch16.png','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (8.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=png::::/sites/dl/free/0077143019/1013351/ch16.png','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (8.0K)</a>
Which cheque may be indicative of kiting? |
|  | A) | Cheque # 1. |
|  | B) | Cheque # 2. |
|  | C) | Cheque # 3. |
|  | D) | Cheque # 4. |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
Which of the following statements is false regarding a four-column bank reconciliation or ‘proof of cash’? |
|  | A) | It is generally prepared by auditors in situations where internal controls in the cash area are considered very weak. |
|  | B) | It can be effective in detecting kiting since cash receipts and disbursements are reconciled with those on the bank statement. |
|  | C) | It can be effective to ensure that all cash disbursements recorded in the entity’s cash disbursements journal have cleared the entity’s bank account. |
|  | D) | It is often used by the auditor to detect certain types of fraud. |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
The auditor typically uses the following procedures to detect fraud in the cash accounts: |
|  | A) | Bank confirmations. |
|  | B) | Bank transfer schedule. |
|  | C) | Bank reconciliation procedures. |
|  | D) | Inquiries of management. |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
Which of the following is true regarding petty cash? |
|  | A) | The petty cash fund should be maintained by someone involved in other cash functions. |
|  | B) | The petty cash fund is almost always the subject of heavy substantive testing. |
|  | C) | Few entities maintain petty cash funds because of the risk of defalcation. |
|  | D) | Auditors typically perform limited testing of the controls over the petty cash fund. |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
Which of the following controls would most effectively ensure that the proper custody of assets in the investing process is maintained? |
|  | A) | Direct access to securities in the safe-deposit box is limited to one corporate officer. |
|  | B) | Personnel who post investment transactions to the general ledger are not permitted to update the investment subsidiary ledger. |
|  | C) | Purchase and sale of investments are executed on the specific authorization of the board of directors. |
|  | D) | The recorded balances in the investment subsidiary ledger are periodically compared with the contents of the safe-deposit box by independent personnel. |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
Key segregations of duties for investments include all of the following except: |
|  | A) | Whoever is responsible for investment activities should not also ensure that all dividend and interest income was received. |
|  | B) | Whoever initiates the purchase of investments should not also grant final approval. |
|  | C) | Whoever oversees security valuation should not also acquire securities. |
|  | D) | Whoever maintains custody of the securities should not also account for the securities. |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
To establish the existence and ownership of an investment in common stock of a public company, an auditor ordinarily performs a security count or |
|  | A) | Determines the market share at the balance sheet date using published quotations. |
|  | B) | Corresponds with the investee regarding the number of shares owned. |
|  | C) | Relies on the internal control structure if the auditor has tested the controls and has reasonable assurance they are operating as prescribed. |
|  | D) | Confirms the number of shares owned with an independent registrar. |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
Which of the following is not a classification of investment securities according to international accounting standards? |
|  | A) | Diversified. |
|  | B) | Held-to-maturity. |
|  | C) | Trading. |
|  | D) | Available-for-sale. |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
An auditor testing long-term investments would ordinarily use substantive analytical procedures to ascertain the reasonableness of the |
|  | A) | Existence of unrealized gains or losses in the portfolio. |
|  | B) | Completeness of recorded investment income. |
|  | C) | Classification between current and non-current portfolios. |
|  | D) | Valuation of marketable equity securities. |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
To establish the existence and rights of a long-term investment in the common stock of a publicly traded company, an auditor ordinarily performs a security count or |
|  | A) | Relies on the entity’s internal controls if the auditor has reasonable assurance that the control activities are being applied as prescribed. |
|  | B) | Confirms the number of shares owned that are held by an independent custodian. |
|  | C) | Determines the market price per share at the balance sheet date from published quotations. |
|  | D) | Confirms the number of shares owned with the issuing company. |
|
|
 |
| 21 |  | 
Which of the following is likely to be the most effective audit procedure for verifying dividends earned on investments in publicly traded equity securities? |
|  | A) | Trace deposits of dividend payments to the cash receipts book. |
|  | B) | Reconcile recorded earnings with the dividend earnings reported in the investment broker statement. |
|  | C) | Compare the amounts received with prior-year dividends received. |
|  | D) | Recompute selected extensions and footings of dividend schedules and compare totals to the general ledger. |
|
|
 |
| 22 |  | 
An auditor would most likely verify the interest earned on bond investments by |
|  | A) | Vouching the receipt and deposit of interest payments. |
|  | B) | Confirming the bond interest rate with the issuer of the bonds. |
|  | C) | Recomputing the interest earned on the basis of face amount, interest rate, and period held. |
|  | D) | Testing the controls over cash receipts. |
|
|
 |
| 23 |  | 
The audit firm’s valuation expert would likely be brought in to assist in the audit of fair value measurements at an entity when the following is present: |
|  | A) | The entity is a new audit client. |
|  | B) | Significant uncertainty exists in key inputs to the entity’s valuation models. |
|  | C) | The entity has a financial instrument with a Level 2 input. |
|  | D) | The entity owns a large and diverse portfolio of publicly traded stock. |
|
|
 |
| 24 |  | 
‘Quoted prices from an active market’ is an example of what level of valuation criteria? |
|  | A) | Level 1. |
|  | B) | Level 3. |
|  | C) | Lower level. |
|  | D) | Basic level. |
|
|

