 |
| 1 |  | 
A simultaneous increase in product price and the price of substitute input capital will: |
|  | A) | increase the demand for labor |
|  | B) | increase the demand for labor if the substitution effect is stronger than the output effect |
|  | C) | increase the demand for labor if the output effect is stronger than the substitution effect |
|  | D) | reduce the demand for labor |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
All else equal, the demand for labor will be least elastic when labor and capital are: |
|  | A) | highly substitutable and labor costs are a small proportion of total costs |
|  | B) | highly substitutable and labor costs are a large proportion of total costs |
|  | C) | not easily substituted and labor costs are a small proportion of total costs |
|  | D) | not easily substituted and labor costs are a large proportion of total costs |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Assume the Apex Manufacturing Company operates in competitive labor and product markets. Its: |
|  | A) | labor demand curve is perfectly elastic at the going wage |
|  | B) | labor demand curve is identical with its marginal product of labor curve |
|  | C) | labor supply curve is perfectly elastic at the going wage |
|  | D) | labor supply curve is upward sloping |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
The demand for carpenters results from the demand for housing. This is an example of: |
|  | A) | the relatively high elasticity of labor demand |
|  | B) | the inverse relationship between the price of labor and the quantity demanded |
|  | C) | the optimal hiring rule for labor |
|  | D) | the derived demand for labor |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
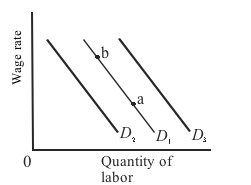
Use the following diagram to answer the next question.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz25b_5.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz25b_5.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a>
Refer to the diagram. Initially, labor demand is given by D1. If labor and capital are complementary inputs, a decrease in the price of capital will cause: |
|  | A) | a shift in labor demand to D2 |
|  | B) | a shift in labor demand to D3 |
|  | C) | either a shift in labor demand to D2 or D3, depending on the relative strengths of the substitution and output effects |
|  | D) | a move from a to b along D1 |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
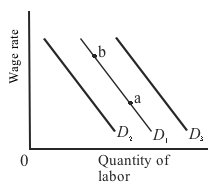
Use the following diagram to answer the next question.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz25b_6.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz25b_6.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
Refer to the diagram. Initially, labor demand is given by D1. A move from D1 to D3 could be caused by either: |
|  | A) | an increase in labor productivity or a decrease in the wage rate |
|  | B) | an increase in the price of a complementary input or a decrease in the wage rate |
|  | C) | a decrease in the price of a substitute input or a decrease in the wage rate |
|  | D) | an increase in labor productivity or an increase in demand for the product this labor is helping to produce |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Other things equal, the demand for labor will be more elastic: |
|  | A) | the greater the demand for the product |
|  | B) | the more substitutable is labor with other inputs |
|  | C) | higher the price of capital |
|  | D) | smaller the elasticity of product demand |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Assume a candle manufacturer is employing two resources L and C in such quantities that the MRPs are $20 and $15, respectively. The prices of the resources are $16 and $12, respectively. This firm: |
|  | A) | is using the least-cost combination of resources to produce its output but should use more of both |
|  | B) | is using the least-cost combination of resources to produce its output but should use less of both |
|  | C) | should use relatively more C |
|  | D) | should use relatively more L |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Suppose an additional unit of labor increases a firm's output from 90 to 100 per hour. If the firm has to reduce its price from $1 to $.99 to sell the additional output, the marginal revenue product of the last worker is: |
|  | A) | $.99 |
|  | B) | $9.00 |
|  | C) | $9.90 |
|  | D) | $10.00 |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
If the price of capital is reduced by 10% and yet a particular firm makes no change in the relative quantities of capital and labor employed, that is, its ratio of capital to labor is unchanged, then: |
|  | A) | the substitution effect is stronger than the output effect |
|  | B) | the demand for labor is perfectly inelastic |
|  | C) | the supply of capital is perfectly elastic |
|  | D) | labor and capital are used in fixed proportions |
|
|

