 |
| 1 |  | 
The "derived demand" concept suggests that an increase in the demand for computers will: |
|  | A) | increase the demand for computer software |
|  | B) | decrease the demand for typewriters |
|  | C) | increase the price of computers |
|  | D) | increase the demand for computer design engineers |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
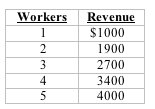
Use the data from the following table for the next question. Selena's Designs sells designer knock-off dresses for $100 each. Selena has discovered the following relationship between the size of her sales staff and her total revenue:
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz25c_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz25c_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a>
Refer to the data. The marginal revenue product of the 5th worker is: |
|  | A) | 6 dresses |
|  | B) | $600 |
|  | C) | $800 |
|  | D) | $4000 |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
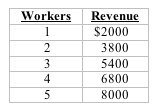
Use the data from the following table for the next question. A law firm has discovered the following relationship between the number of junior associates and its total revenue.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz25c_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz25c_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a>
Refer to the data. If the market pay for a junior associate is $1500, the law firm should hire: |
|  | A) | 2 associates |
|  | B) | 3 associates |
|  | C) | 4 associates |
|  | D) | 5 associates |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Suppose labor's MRP at a particular firm is $20 and the market wage for each worker is $15. If this firm is hiring labor from a purely competitive market, then: |
|  | A) | the firm is making $5 profit for each worker hired |
|  | B) | laying off a worker would increase the firm's profit (or reduce its losses) by $5 |
|  | C) | by hiring another worker, the firm could increase its profits (or reduce its losses) by $5 |
|  | D) | the firm should expand employment until the wage rises to $20 |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
For a firm that both sells its output and buys its inputs in purely competitive markets, the labor demand curve: |
|  | A) | slopes downward and the labor supply curve is perfectly elastic |
|  | B) | slopes downward and the labor supply curve is upward sloping |
|  | C) | is perfectly elastic and the labor supply curve is upward sloping |
|  | D) | is perfectly elastic and the labor supply curve is perfectly inelastic |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Two firms, X and Y, have exactly the same marginal product of labor schedules and both sell their output at a price of $2.00. If X's short-run labor demand curve is more elastic than Y's short-run labor demand curve, we can conclude that: |
|  | A) | X is not maximizing profits |
|  | B) | X in an imperfectly competitive seller |
|  | C) | Y should hire more labor |
|  | D) | Y is an imperfectly competitive seller |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
An increase in the price of jet fuel increases the cost of airline travel and reduces the demand for airplane mechanics. This decrease in labor demand would be caused by which change in a determinant of labor demand? |
|  | A) | A fall in labor productivity |
|  | B) | An increase in product demand |
|  | C) | A decrease in product demand |
|  | D) | An increase in the price of another resource |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Other things equal, a firm's demand for unskilled labor will be more elastic than its demand for skilled labor if: |
|  | A) | the cost of unskilled labor is a smaller proportion of total cost than the cost of skilled labor |
|  | B) | the demand for the product is elastic |
|  | C) | it is easier to substitute capital for unskilled labor than for skilled labor |
|  | D) | skilled labor and unskilled labor must be used in direct proportion to one another |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
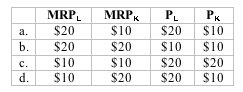
Assume that a purely competitive firm uses only labor and capital to produce a service. Which of the following resource combinations is consistent with maximum profits?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz25c_9.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (8.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz25c_9.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (8.0K)</a>
|
|  | A) | A |
|  | B) | B |
|  | C) | C |
|  | D) | D |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
A purely competitive firm is paying twice as much for labor per unit as for capital. Although the average productivity of labor is twice that of capital, their marginal products are the same. In order to minimize cost, this firm: |
|  | A) | should use relatively more capital |
|  | B) | should use relatively more labor |
|  | C) | should use both more labor and more capital |
|  | D) | is using the correct proportion of labor and capital |
|
|

