 |
| 1 |  | 
Which of the following describes excess capacity? |
|  | A) | The difference between what is being produced and the level of production that maximizes profits |
|  | B) | The difference between what is being produced and economic capacity |
|  | C) | The difference between what is being produced and the level of production that minimizes short-run marginal cost |
|  | D) | The difference between the level of production that minimizes short-run average cost and that which achieves economic capacity |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Which of the following statements is correct when comparing a monopoly market and an oligopoly market? |
|  | A) | The price and quantity would be the same in both markets. |
|  | B) | Both price and quantity would be lower in the monopoly market than in the oligopoly market. |
|  | C) | The price would be lower and the quantity would be higher in the monopoly market than in the oligopoly market. |
|  | D) | The price would be higher and the quantity would be lower in the monopoly market than in the oligopoly market. |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
All, except one, of the following statements about the kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly are correct. Which is the exception? |
|  | A) | It explains why the prices charged by rival firms are often similar. |
|  | B) | It explains why rival firms that charge similar prices may not be in collusion. |
|  | C) | It explains why the prices charged by rival firms sometimes go for months, or even years, without changing. |
|  | D) | It explains, particularly well, how the prevailing price in the industry first got established. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
If we assume that price leadership prevails in a particular industry, what might prevent the leader from announcing a dramatic increase in the price of the product sold? |
|  | A) | The fear that the AC of the other firms within the industry would decrease |
|  | B) | The fear that new firms would be tempted to enter the industry |
|  | C) | The fear that one of the other firms would break ranks and increase their price even more |
|  | D) | The fear that such action would provide proof that the firms are engaged in overt collusion |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
All of the following, except one, could explain a price war between firms. Which is the exception? |
|  | A) | A breakdown in the collusive agreement between firms |
|  | B) | The intense competition that one finds in a perfectly competitive industry |
|  | C) | An aggressive young firm challenging the established price leadership of a rival firm |
|  | D) | The action taken by established firms to ward off the possible entry of a new firm |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
All, except one, of the following statements are valid arguments in favour of advertising. Which one is the exception? |
|  | A) | Advertising provides consumers with information. |
|  | B) | Advertising reduces the search time needed by consumers to acquire products. |
|  | C) | Advertising increases the barriers to entry into an industry and thereby enhances competition. |
|  | D) | Advertising can lower the prices of products by reducing the firms’ average cost through increased output levels. |
|  | E) | Advertising increases the availability of radio and television program choices for the consumer. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
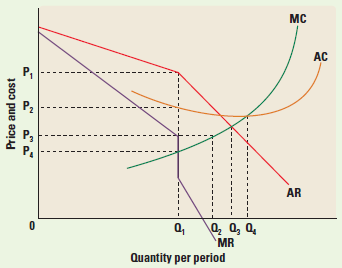 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=png::::/sites/dl/free/1259030687/1059313/SayreMicro8ce_ch11.PNG','popWin', 'width=392,height=338,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=png::::/sites/dl/free/1259030687/1059313/SayreMicro8ce_ch11.PNG','popWin', 'width=392,height=338,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a>What output level will the firm produce? |
|  | A) | Q1 |
|  | B) | Q2 |
|  | C) | Q3 |
|  | D) | Q4 |
|  | E) | More information is needed to answer this question |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=png::::/sites/dl/free/1259030687/1059313/SayreMicro8ce_ch11.PNG','popWin', 'width=392,height=338,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=png::::/sites/dl/free/1259030687/1059313/SayreMicro8ce_ch11.PNG','popWin', 'width=392,height=338,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a>What price will the firm charge? |
|  | A) | P1 |
|  | B) | P2 |
|  | C) | P3 |
|  | D) | P4 |
|
|

