| The Investigation poses questions to generate interest in various
mathematical topics from the text and encourages students to formulate
and investigate their own conjectures. One use of the investigations is
for term papers in which students report on their conjectures and the
patterns they find.
Click on the Word file below to begin the investigation:
 Read Me - Inscribed Angles in Circles Instructions (Word Format)
(46.0K) Read Me - Inscribed Angles in Circles Instructions (Word Format)
(46.0K)
Laboratory Investigation 9.2Inscribed Angles in Circles*- Draw a circle and select any 2 points A and B on its circumference which are not the endpoints of a diameter (see figure). Then select a different point V on the circumference and draw AVB. This is called an inscribed angle because the vertex of the angle is on the circle and and are chords of the circle. What can be said about the measure of such angles as point V moves to different locations on the circumference and points A and B remain fixed?
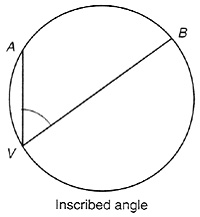 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072532947/78543/LI_9_2a.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (25.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072532947/78543/LI_9_2a.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (25.0K)</a>- A central angle of a circle has its vertex at the center of the circle, as shown in the following figure.
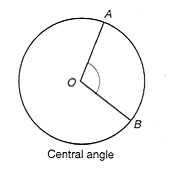 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072532947/78543/LI_9_2b.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (20.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072532947/78543/LI_9_2b.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (20.0K)</a>- Draw a circle and select any 4 point on the circumference as the vertices of a quadrilateral. Measure the pairs of opposite angles of the quadrilateral and look for relationships. Move the vertices on the circle to see if your relationships hold. Will such relationships hold for an arbitrary quadrilateral whose vertices are not on the circumference of a circle?
*This investigation may be carried out with software such as Cabri Geometry II, Geometer's Sketch Pad, or The Geometric Super Supposer.
|


