Please note that this quiz uses special characters. Not all browsers display special characters properly. For best results please use Internet Explorer 5.5 or newer or Netscape 6.2 or newer.
 |
| 1 |  | 
A radioisotope decays to give an alpha particle and Th-234. What was the original element? |
|  | A) | Pa |
|  | B) | Bi |
|  | C) | U |
|  | D) | Ra |
|  | E) | Rn |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
When Pb-210 decays by emission of a b particle, what isotope is formed? |
|  | A) | Bi-209 |
|  | B) | Bi-210 |
|  | C) | Pb-209 |
|  | D) | Tl-210 |
|  | E) | Tl-209 |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
The nuclide copper-64 decays by emission of a positron. What is the product nuclide? |
|  | A) | 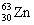 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image14.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image14.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|
|  | B) | 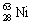 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image15.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image15.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|
|  | C) | 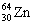 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image16.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image16.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|
|  | D) | 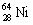 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image17.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image17.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|
|  | E) | 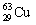 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image18.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image18.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Given that potassium-39 is a stable nuclide, what type of particle would you expect to be emitted when potassium-42 decays? |
|  | A) | proton |
|  | B) | neutron |
|  | C) | beta particle |
|  | D) | positron |
|  | E) | alpha particle |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
What fraction of radioactive atoms remains in a sample after three half-lives? |
|  | A) | 1/4 |
|  | B) | 1/5 |
|  | C) | 1/6 |
|  | D) | 1/8 |
|  | E) | none of the above |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
What is the specific activity (in Ci/g) of radioactive sample if 4.56 mg emits 2.27 ´ 108 b particles per second? |
|  | A) | 4.97 Ci/g |
|  | B) | 0.135 Ci/g |
|  | C) | 1.35 Ci/g |
|  | D) | 0.00133 Ci/g |
|  | E) | none of the above |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Tritium (hydrogen-3) is a naturally-occurring isotope, present in water, and has a half-life of 12.3 years. A bottle of aged red wine has a tritium activity which is three-quarters as great as in newly-bottled wine. Estimate or calculate the age of the wine. |
|  | A) | 16.4 years |
|  | B) | 9.3 years |
|  | C) | 8.9 years |
|  | D) | 5.1 years |
|  | E) | 3.1 years |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
When atoms of aluminum-27 are bombarded with alpha particles, a neutron and an isotope of phosphorus are produced. What is the mass number of the isotope? |
|  | A) | 28 |
|  | B) | 29 |
|  | C) | 30 |
|  | D) | 31 |
|  | E) | 32 |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Gamma-rays and X-rays interact with matter, causing |
|  | A) | formation of ions, but no free radicals. |
|  | B) | formation of free radicals, but no ions. |
|  | C) | nuclear transmutation reactions. |
|  | D) | formation of ions and free radicals. |
|  | E) | formation of ions and nuclear transmutation reactions. |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
For the average person, what is the source of the greatest amount of radiation per year? |
|  | A) | radiation from the air, especially radon gas |
|  | B) | medical and dental X-rays |
|  | C) | cosmic rays |
|  | D) | potassium-40 in the body |
|  | E) | nuclear power plants and their spent fuel |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Considering the most stable isotope of each of the following elements, predict which one has the highest binding energy per nucleon. |
|  | A) | hydrogen |
|  | B) | beryllium |
|  | C) | lithium |
|  | D) | uranium |
|  | E) | cobalt |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
The atomic mass of manganese-55 is 54.938 amu. Use data from your textbook to determine the total binding energy of this nuclide, in J/atom. |
|  | A) | 2.58 ´ 10-19 J |
|  | B) | 4.65 ´ 1016 J |
|  | C) | 1.33 ´ 10-19 J |
|  | D) | 7.74 ´ 10-11 J |
|  | E) | None of the above |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
Which of the following cannot be an example of nuclear fusion? |
|  | A) | A nuclear reaction in which two reactants have greater binding energy than their fused product. |
|  | B) | A nuclear reaction in which a carbon nucleus is produced. |
|  | C) | The primary energy-producing reaction in the Sun. |
|  | D) | The primary energy-producing reaction in a hydrogen bomb. |
|  | E) | A reaction in which the reactants are less stable than the products. |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
A typical neutron-initiated fission of U-235 yields Mo-97, two neutrons, and another element. What is this second element? |
|  | A) | In |
|  | B) | Te |
|  | C) | Sn |
|  | D) | Sb |
|  | E) | La |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
Which of the following are present in a nuclear reactor in order to slow the rate of the chain reaction? |
|  | A) | reflectors |
|  | B) | control rods |
|  | C) | moderators |
|  | D) | heavy water |
|  | E) | zirconium |
|
|

