 |
| 1 |  | 
The Agricultural Adjustment Act of 1933: |
|  | A) | allowed individuals to acquire farmland from the federal government if they consented to "homestead" |
|  | B) | began the federal practice of subsidizing crops produced for export |
|  | C) | established maximum prices farmers have to pay for fertilizer, seed, and other basic inputs |
|  | D) | established the parity concept as a basis for agricultural policy |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Use the following diagram to answer the next question.
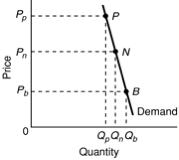 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz31a_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=229,height=230,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz31a_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=229,height=230,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>
Refer to the diagram. Qp, Qn and Qb correspond to poor, normal, and bumper crop levels, respectively. Compared to a normal year, if farmers produce a bumper crop, gross farm income will: |
|  | A) | increase because demand is elastic |
|  | B) | decrease because demand is inelastic |
|  | C) | increase because demand is inelastic |
|  | D) | decrease because demand is inelastic |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
The demand for most agricultural products: |
|  | A) | has decreased over time as incomes have increased |
|  | B) | has increased at the same rate as the increase in the population |
|  | C) | has increased slower than the increase in supply |
|  | D) | is elastic |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
All of the following are outcomes of U.S. farm price supports, except: |
|  | A) | world agricultural prices increase |
|  | B) | tariffs or quotas are necessary to prevent increased imports of agricultural products |
|  | C) | higher taxes are required to pay for government purchases of surplus production |
|  | D) | export earnings of developing countries are reduced |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
In 1994, the nations belonging to the World Trade Organization agreed to reduce farm price support programs in order to: |
|  | A) | increase the amount of money available for foreign aid |
|  | B) | reduce agricultural overproduction by developing countries |
|  | C) | reduce economic distortions and international misallocation of agricultural resources |
|  | D) | reduce government deficits worldwide |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
The 1996 law ending price supports on wheat, corn, and other crops was known as the: |
|  | A) | Parity Act |
|  | B) | Freedom to Farm Act |
|  | C) | Farm Act |
|  | D) | Farmer Independence Act |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
If in a certain year the indices of prices received and paid by farmers were 120 and 150, respectively, the parity ratio would be: |
|  | A) | 30 |
|  | B) | 125 |
|  | C) | 20 |
|  | D) | 80 |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
U.S. agricultural price supports: |
|  | A) | increase domestic quantity demanded |
|  | B) | make domestic demand more inelastic |
|  | C) | disproportionately benefit large farmers |
|  | D) | reduce agricultural imports |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
The average income of farm households is substantially below that of non-farm households. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
For farm products in the aggregate, demand elasticity is between: |
|  | A) | .01 and .02 |
|  | B) | .2 and .25 |
|  | C) | .9 and 1.0 |
|  | D) | 1.5 and 1.6 |
|
|

