 |
| 1 |  | 
Because the marginal utility of food diminishes rapidly: |
|  | A) | the supply of agricultural products is elastic |
|  | B) | the supply of agricultural products is inelastic |
|  | C) | the demand for agricultural products is elastic |
|  | D) | the demand for agricultural products is inelastic |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
The demand for barley is inelastic. Accordingly, barley farmers' aggregate income will: |
|  | A) | rise in high-yield years and fall in low-yield years |
|  | B) | rise in low-yield years and fall in high-yield years |
|  | C) | rise over time |
|  | D) | fall over time |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
U.S. farmers' incomes are unstable in the short run, primarily owing to: |
|  | A) | changes in price support programs with each new congress |
|  | B) | fluctuations in U.S. agricultural imports that have caused wide swings in prices of food products |
|  | C) | swings in crop yields and export demand, coupled with inelastic demand |
|  | D) | rapid changes in technology coupled with slow population growth |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Because farmers' fixed costs are high compared to their variable costs, short-run farm production is relatively insensitive to price changes. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Over the long-run, the number of farm households has declined in part because: |
|  | A) | the demand for farm products is price-elastic |
|  | B) | the demand for farm products is inelastic with respect to both price and income |
|  | C) | farm productivity has increased at a much slower pace than in the manufacturing and service sectors |
|  | D) | government policies have resulted in chronic shortages in critical markets |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Since 1960, total farm employment has: |
|  | A) | decreased both absolutely and as a proportion of total employment |
|  | B) | increased absolutely, but decreased as a proportion of total employment |
|  | C) | remained about the same, but decreased as a proportion of total employment |
|  | D) | fallen in relation to manufacturing employment, but risen in relation to service employment |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Which best expresses the concept of parity? |
|  | A) | Total farm employment should remain the same over time |
|  | B) | Agricultural prices should remain constant over time |
|  | C) | Farm income should increase at the same rate as the total population |
|  | D) | Prices of farm products should increase at the same rate as the prices farmers pay for goods and services |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Use the following diagram of the corn market to answer the next question. Assume both the demand and the supply of corn are inelastic.
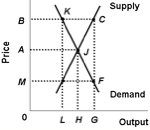 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz31c_8.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz31c_8.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a>
Refer to the diagram. If the government supports price B in this market, all of the following will result except: |
|  | A) | a surplus of LG is created |
|  | B) | total farm income increases from OAJH to OBCG |
|  | C) | government transfers LKCG from taxpayers to farmers |
|  | D) | aggregate consumer expenditures on corn decrease |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Which of the following government programs stimulates demand in order to reduce agricultural surpluses created by farm subsidies? |
|  | A) | Farm Act of 2002 |
|  | B) | Food for Peace |
|  | C) | Freedom to Farm Act of 1996 |
|  | D) | Import quotas and tariffs |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
U.S. farm policy: |
|  | A) | lowers the price of farm land, hurting landowners relative to tenant farmers |
|  | B) | directs farm aid disproportionately to high-income farmers |
|  | C) | provides retraining and transitional support to farmers willing to leave the industry |
|  | D) | results in an underallocation of resources to farming |
|
|

