 |
| 1 |  | 
Which of the following policies is most likely to prevent a fisheries collapse? |
|  | A) | Limits on the number of days per year that a species can be caught |
|  | B) | Limits on the number of boats allowed to fish in a particular area |
|  | C) | Removing individual property rights to a species and transferring such rights to the government |
|  | D) | Limits on the total allowable catch for a particular species |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Which of the following best explains the movement of the commodity price index over the last 100 years? |
|  | A) | The index has fallen because the supply of commodities has increased faster than the demand for them |
|  | B) | The index has fallen because the demand for commodities has increased faster than the supply of them |
|  | C) | The index has risen because the supply of commodities has fallen while the demand has risen |
|  | D) | The index has fallen because the demand for commodities has fallen while the supply has risen |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Over the last 25 years, U.S. energy efficiency has: |
|  | A) | worsened; per capita energy inputs have increased while per capita real GDP has leveled off |
|  | B) | worsened; the ratio of real GDP to BTUs used has decreased |
|  | C) | improved; per capita energy inputs have leveled off while per capita real GDP has increased |
|  | D) | improved; while per capita real GDP has fallen, per capita energy use has fallen even faster |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Which of the following sources accounted for the greatest proportion of U.S. electricity generation in 2004? |
|  | A) | Nuclear |
|  | B) | Solar |
|  | C) | Natural gas |
|  | D) | Coal |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Changing attitudes towards religion, expanded career opportunities for women, mandatory schooling, and restrictive child-labor laws all help to explain: |
|  | A) | rising fertility rates |
|  | B) | falling fertility rates |
|  | C) | falling death rates |
|  | D) | rising population growth |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
By discounting the future, present value calculations imply that a resource will be used up sooner than is optimal. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
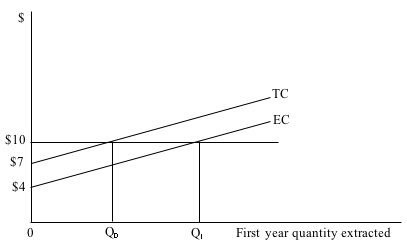
Refer to the following:
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz27webb_7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz27webb_7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>
If EC represents the extraction cost and TC the total cost of extracting a particular amount, the user cost of this non-renewable resource is: |
|  | A) | $3 |
|  | B) | $5 |
|  | C) | $7 |
|  | D) | $10 |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Suppose a coal mining firm predicts that the demand for coal (and hence its price) will grow faster than previous forecasts had indicated. This change in outlook will: |
|  | A) | increase the current user cost of coal and increase the current rate of extraction |
|  | B) | increase the current user cost of coal and decrease the current rate of extraction |
|  | C) | decrease the current user cost of coal and increase the current rate of extraction |
|  | D) | decrease the current user cost of coal and decrease the current rate of extraction |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
In attempting to minimize costs, a fundamental problem facing electricity generating companies is that: |
|  | A) | power plants with the lowest operating costs per kilowatt hour tend to have the highest fixed construction costs |
|  | B) | federal law limits mixing generator technologies in a given utility district |
|  | C) | the prices of various energy sources is highly variable over the year, but the demand for them is stable |
|  | D) | marginal cost exceeds average cost for all reasonable output levels |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Which of the following best represents the text authors' views regarding the possibility that the demand for resources will exhaust their supply? |
|  | A) | Growing population and rising incomes will cause the demand for resources to exhaust their supply sometime over the next two hundred years |
|  | B) | Though population growth will feed demand for resources, such growth will reduce per capita income. These two effects will likely cancel, reducing the likelihood of chronic resource shortages |
|  | C) | Despite increased demand as poor countries begin to develop, technological advance and falling population growth rates make such a possibility unlikely |
|  | D) | While many local areas will have plenty of resources, global resource demand will exceed supply |
|
|

